Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches to Analyze and Detect COVID-19: A Review
- PMID: 33899005
- PMCID: PMC8056995
- DOI: 10.1007/s42979-021-00605-9
Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches to Analyze and Detect COVID-19: A Review
Abstract
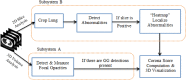
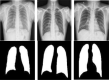
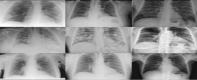
COVID-19 also referred to as Corona Virus disease is a communicable disease that is caused by a coronavirus. Significant number of people who are tainted with this infection will have to brave and encounter moderate to severe respiratory sickness. Aged persons, sick, convalescing people and all those having underlying health complications like diabetes, chronic breathing diseases and cardiovascular diseases are bound to contract this sickness if not taken proper care of. At the current scenario, there are neither definite treatments nor inoculations against COVID-19. Nevertheless, there are numerous continuing clinical trials assessing the impending treatments and vaccines. Sensing the threatening impacts of Covid-19, researchers of computer science have started using various techniques and approaches of Machine Learning and Deep Learning to detect the presence of the disease using X-rays and CT images. The biggest stumbling block here is that there are only a few datasets available. There is also less number of experts for marking the information explicit to this new strain of infection in people. Artificial Intelligence centred tools can be designed and developed quickly for adapting the existing AI models and for leveraging the ability to modify and associating them with the preliminary clinical understanding to address the new group of COVID-19 and the novel challenges associated with it. In this paper, we look into a few techniques of Machine Learning and Deep Learning that have been employed to analyse Corona Virus Data.
Keywords: CT images; CheXNet; Convolutional neural network; Corona virus; Covid-19; Covid-net; Deep learning; IRCNN; Machine learning.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd 2021.
Figures
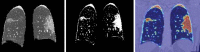
References
-
- Ophir G et al. Rapid AI development cycle for the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: initial results for automated detection & patient monitoring using deep learning CT image analysis. In: Radiology- Artificial Intelligence, arXiv:2003.05037 [eess.IV] 2020.
-
- Md Zahangir A et al. COVID_MTNet: COVID-19 detection with multi-task deep learning approaches. In: arXiv:2004.03747 [eess.IV], 2020.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
