Dietary conjugated linoleic acid links reduced intestinal inflammation to amelioration of CNS autoimmunity
- PMID: 33899089
- PMCID: PMC8105041
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awab040
Dietary conjugated linoleic acid links reduced intestinal inflammation to amelioration of CNS autoimmunity
Abstract
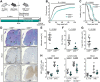
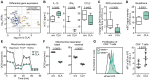
A close interaction between gut immune responses and distant organ-specific autoimmunity including the CNS in multiple sclerosis has been established in recent years. This so-called gut-CNS axis can be shaped by dietary factors, either directly or via indirect modulation of the gut microbiome and its metabolites. Here, we report that dietary supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid, a mixture of linoleic acid isomers, ameliorates CNS autoimmunity in a spontaneous mouse model of multiple sclerosis, accompanied by an attenuation of intestinal barrier dysfunction and inflammation as well as an increase in intestinal myeloid-derived suppressor-like cells. Protective effects of dietary supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid were not abrogated upon microbiota eradication, indicating that the microbiome is dispensable for these conjugated linoleic acid-mediated effects. Instead, we observed a range of direct anti-inflammatory effects of conjugated linoleic acid on murine myeloid cells including an enhanced IL10 production and the capacity to suppress T-cell proliferation. Finally, in a human pilot study in patients with multiple sclerosis (n = 15, under first-line disease-modifying treatment), dietary conjugated linoleic acid-supplementation for 6 months significantly enhanced the anti-inflammatory profiles as well as functional signatures of circulating myeloid cells. Together, our results identify conjugated linoleic acid as a potent modulator of the gut-CNS axis by targeting myeloid cells in the intestine, which in turn control encephalitogenic T-cell responses.
Keywords: conjugated linoleic acid; dietary supplementation; gut–CNS axis; intestinal inflammation; multiple sclerosis.
© The Author(s) (2021). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dietary tryptophan links encephalogenicity of autoreactive T cells with gut microbial ecology.Nat Commun. 2019 Oct 25;10(1):4877. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12776-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31653831 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary conjugated linoleic acid modulates morphology, selective immune parameters, and gene expressions in the intestine of grass carp.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Mar;86:536-548. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.11.071. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30508674
-
Consumption of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)-supplemented diet during colitis development ameliorates gut inflammation without causing steatosis in mice.J Nutr Biochem. 2018 Jul;57:238-245. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 27. J Nutr Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29800810
-
Modulation of inflammation and immunity by dietary conjugated linoleic acid.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 15;785:87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.095. Epub 2015 May 15. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 25987426 Review.
-
Biological effects of conjugated linoleic acids supplementation.Pol J Vet Sci. 2012;15(2):403-8. doi: 10.2478/v10181-012-0063-x. Pol J Vet Sci. 2012. PMID: 22844724 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting gut microbiota: new therapeutic opportunities in multiple sclerosis.Gut Microbes. 2023 Dec;15(2):2274126. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2274126. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 37979154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Antioxidant Effect of Dietary Bioactives Arises from the Interplay between the Physiology of the Host and the Gut Microbiota: Involvement of Short-Chain Fatty Acids.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 10;12(5):1073. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051073. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CNS Pericytes Modulate Local T Cell Infiltration in EAE.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 28;23(21):13081. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113081. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361868 Free PMC article.
-
Staged suppression of microglial autophagy facilitates regeneration in CNS demyelination by enhancing the production of linoleic acid.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jan 3;120(1):e2209990120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2209990120. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36577069 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary wheat amylase trypsin inhibitors exacerbate CNS inflammation in experimental multiple sclerosis.Gut. 2023 Dec 7;73(1):92-104. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-329562. Gut. 2023. PMID: 37595983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amato MP, Derfuss T, Hemmer B, et al.Environmental modifiable risk factors for multiple sclerosis: report from the 2016 ECTRIMS focused workshop. Mult Scler J. 2018;24:590-603. - PubMed
-
- Haghikia A, Jörg S, Duscha A, et al.Dietary fatty acids directly impact central nervous system autoimmunity via the small intestine. Immunity. 2015;43:817-829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

