CD19 CAR-T cell treatment conferred sustained remission in B-ALL patients with minimal residual disease
- PMID: 33899130
- PMCID: PMC8571234
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-021-02941-4
CD19 CAR-T cell treatment conferred sustained remission in B-ALL patients with minimal residual disease
Abstract
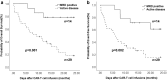
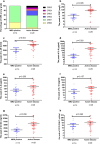
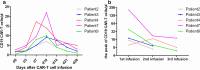
The persistence or recurrence of minimal residual disease (MRD) after chemotherapy predicts relapse of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T (CD19 CAR-T) cells have shown promising responses in B-ALL. However, their role in chemotherapy-refractory MRD-positive B-ALL remains unclear. Here we aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of CD19 CAR-T cells in MRD-positive B-ALL patients. From January 2018, a total of 14 MRD-positive B-ALL patients received one or more infusions of autogenous CD19 CAR-T cells. Among them, 12 patients achieved MRD-negative remission after one cycle of CAR-T infusion. At a median follow-up time of 647 days (range 172-945 days), the 2-year event-free survival rate in MRD-positive patients was 61.2% ± 14.0% and the 2-year overall survival was 78.6 ± 11.0%, which were significantly higher than patients with active disease (blasts ≥ 5% or with extramedullary disease). Moreover, patients with MRD had a lower grade of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) than patients with active disease. However, the peak expansion of CAR-T cells in MRD positive patients showed no statistical difference compared to patients with active disease. Five patients received two or more CAR-T cell infusions and these patients showed a decreased peak expansion of CAR-T cell in subsequent infusions. In conclusion, pre-emptive CD19 CAR-T cell treatment is an effective and safe approach and may confer sustained remission in B-ALL patients with chemotherapy-refractory MRD. The trials were registered at www.chictr.org.cn as ChiCTR-ONN-16009862 (November 14, 2016) and ChiCTR1800015164 (March 11, 2018).
Keywords: B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T cells; Cytokine release syndrome; Minimal residual disease; Relapse.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bassan R, Bruggemann M, Radcliffe HS, Hartfield E, Kreuzbauer G, Wetten S. A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of minimal residual disease as a prognostic indicator in adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2019;104(10):2028–2039. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.201053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raff T, Gokbuget N, Luschen S, Reutzel R, Ritgen M, Irmer S, Bottcher S, Horst HA, Kneba M, Hoelzer D, Bruggemann M, Group GS Molecular relapse in adult standard-risk ALL patients detected by prospective MRD monitoring during and after maintenance treatment: data from the GMALL 06/99 and 07/03 trials. Blood. 2007;109(3):910–915. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-037093. - DOI - PubMed
-
- He X, Xiao X, Li Q, Jiang Y, Cao Y, Sun R, Jin X, Yuan T, Meng J, Ma L, Lu W, Lyu C, Liu K, Zhao M. Anti-CD19 CAR-T as a feasible and safe treatment against central nervous system leukemia after intrathecal chemotherapy in adults with relapsed or refractory B-ALL [letter] Leukemia. 2019;33(8):2102–2104. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0437-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

