2021 ISHEN guidelines on animal models of hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 33900013
- PMCID: PMC9812338
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.14911
2021 ISHEN guidelines on animal models of hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
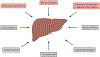
This working group of the International Society of Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) was commissioned to summarize and update current efforts in the development and characterization of animal models of hepatic encephalopathy (HE). As defined in humans, HE in animal models is based on the underlying degree and severity of liver pathology. Although hyperammonemia remains the key focus in the pathogenesis of HE, other factors associated with HE have been identified, together with recommended animal models, to help explore the pathogenesis and pathophysiological mechanisms of HE. While numerous methods to induce liver failure and disease exist, less have been characterized with neurological and neurobehavioural impairments. Moreover, there still remains a paucity of adequate animal models of Type C HE induced by alcohol, viruses and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; the most common etiologies of chronic liver disease.
Keywords: acute liver failure; behaviour; bile duct ligation; chronic liver disease; hepatic encephalopathy; hyperammonemia; liver toxins; neurological deficits; portocaval anastomosis.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement:
SD: nothing to disclose
CC: nothing to disclose
ND: nothing to disclose
ARJ: nothing to disclose
CFR: Christopher F. Rose has research collaborations with Mallinckrodt Pharma and Neuractas and is an advisor for Axcella, Horizon Therapeutics, Lupin Pharma, Morphocell Technologies, and Neuractas.
Figures


References
-
- Cabrera-Pastor A, Llansola M, Montoliu C, et al. Peripheral inflammation induces neuroinflammation that alters neurotransmission and cognitive and motor function in hepatic encephalopathy: Underlying mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019;226(2):e13270. - PubMed
-
- Bosoi CR, Rose CF. Oxidative stress: a systemic factor implicated in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2013;28(2):175–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

