Evaluating Differences in Whole Blood, Serum, and Urine Screening Tests for Zika Virus, Puerto Rico, USA, 2016
- PMID: 33900183
- PMCID: PMC8084515
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2705.203960
Evaluating Differences in Whole Blood, Serum, and Urine Screening Tests for Zika Virus, Puerto Rico, USA, 2016
Abstract
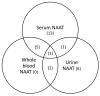
We evaluated nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) for Zika virus on whole-blood specimens compared with NAAT on serum and urine specimens among asymptomatic pregnant women during the 2015-2016 Puerto Rico Zika outbreak. Using NAAT, more infections were detected in serum and urine than in whole blood specimens.
Keywords: NAAT; PCR; Puerto Rico; United States; Zika virus; mosquito-borne diseases; mosquitos; nucleic acid amplification testing; outbreak; pregnancy; vector-borne diseases; viruses; whole blood; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Testing guidance: new Zika and dengue testing guidance (updated November 2019) [cited 2020 Jul 14]. https://www.cdc.gov/zika/hc-providers/testing-guidance.html
-
- Oduyebo T, Polen KD, Walke HT, Reagan-Steiner S, Lathrop E, Rabe IB, et al. Update: interim guidance for health care providers caring for pregnant women with possible Zika virus exposure—United States (including U.S. territories), July 2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:781–93. 10.15585/mmwr.mm6629e1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical