C/EBPα is indispensable for PML/RARα-mediated suppression of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells
- PMID: 33901013
- PMCID: PMC8148485
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203000
C/EBPα is indispensable for PML/RARα-mediated suppression of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells
Abstract
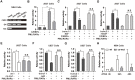
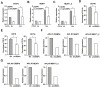
Better understanding of the transcriptional regulatory network in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cells is critical to illustrate the pathogenesis of other types of acute myeloid leukemia. Previous studies have primarily focused on the retinoic acid signaling pathway and how it is interfered with by promyelocytic leukemia/retinoic acid receptor-α (PML/RARα) fusion protein. However, this hardly explains how APL cells are blocked at the promyelocytic stage. Here, we demonstrated that C/EBPα bound and transactivated the promoter of long non-coding RNA NEAT1, an essential element for terminal differentiation of APL cells, through C/EBP binding sites. More importantly, PML/RARα repressed C/EBPα-mediated transactivation of NEAT1 through binding to NEAT1 promoter. Consistently, mutation of the C/EBP sites or deletion of retinoic acid responsive elements (RAREs) and RARE half motifs abrogated the PML/RARα-mediated repression. Moreover, silencing of C/EBPα attenuated ATRA-induced NEAT1 upregulation and APL cell differentiation. Finally, simultaneous knockdown of C/EBPα and C/EBPβ reduces ATRA-induced upregulation of C/EBPε and dramatically impaired NEAT1 activation and APL cell differentiation. In sum, C/EBPα binds and transactivates NEAT1 whereas PML/RARα represses this process. This study describes an essential role for C/EBPα in PML/RARα-mediated repression of NEAT1 and suggests that PML/RARα could contribute to the pathogenesis of APL through suppressing C/EBPα targets.
Keywords: APL; C/EBPα; NEAT1; PML/RARα; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
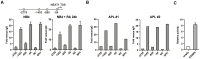

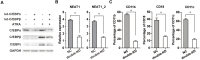
References
-
- Hoemme C, Peerzada A, Behre G, Wang Y, McClelland M, Nieselt K, Zschunke M, Disselhoff C, Agrawal S, Isken F, Tidow N, Berdel WE, Serve H, Müller-Tidow C. Chromatin modifications induced by PML-RARalpha repress critical targets in leukemogenesis as analyzed by ChIP-Chip. Blood. 2008; 111:2887–95. 10.1182/blood-2007-03-079921 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grignani F, De Matteis S, Nervi C, Tomassoni L, Gelmetti V, Cioce M, Fanelli M, Ruthardt M, Ferrara FF, Zamir I, Seiser C, Grignani F, Lazar MA, et al. Fusion proteins of the retinoic acid receptor-alpha recruit histone deacetylase in promyelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1998; 391:815–18. 10.1038/35901 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

