Histiocytosis
- PMID: 33901419
- PMCID: PMC9364113
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00311-1
Histiocytosis
Abstract
Histiocytoses constitute a heterogeneous group of rare disorders, characterised by infiltration of almost any organ by myeloid cells with diverse macrophage or dendritic cell phenotypes. Histiocytoses can start at any age. Diagnosis is based on histology in combination with appropriate clinical and radiological findings. The low incidence and broad spectrum of clinical manifestations often leads to diagnostic delay, especially for adults. In most cases, biopsy specimens infiltrated by histiocytes have somatic mutations in genes activating the MAP kinase cell-signalling pathway. These mutations might also be present in blood cells and haematopoietic progenitors of patients with multisystem disease. A comprehensive range of investigations and molecular typing are essential to accurately predict prognosis, which can vary from spontaneous resolution to life-threatening disseminated disease. Targeted therapies with BRAF or MEK inhibitors have revolutionised salvage treatment. However, the type and duration of treatment are still debated, and the prevention of neurological sequelae remains a crucial issue.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests OA-W reports personal fees from Envisagenics, Pfizer Boulder, AIChemy, Janssen, Merck, H3 Biomedicine, Prelude Therapeutics, and Foundation Medicine, and grants from LOXO Oncology, during the conduct of the study. FC-A and JH are investigators (FC-A being the principal investigator) of an academic study on the efficacy of cobimetinib for treating histiocytoses (COBRAH, NCT 04007848). AI reports grants, research support, and travel funding from Carthera; grants from Transgene, Sanofi, Air Liquide, and Nutritheragene; personal fees from Novocure; and personal fees and travel funding from Leo Pharma, outside the submitted work. BJR received reimbursement for travel and lodging expenses from Eli Lilly and Company. JD reports grants from X4 Pharmaceuticals, outside the submitted work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
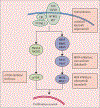
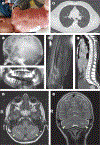
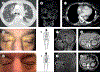
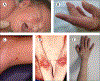
Comment in
-
IgG4-related disease and Rosai-Dorfman-Destombes disease.Lancet. 2021 Oct 2;398(10307):1213-1214. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01812-2. Lancet. 2021. PMID: 34600619 No abstract available.
References
-
- Writing Group of the Histiocyte Society. Histiocytosis syndromes in children. Lancet 1987; 1: 208–09. - PubMed
-
- Haroche J, Cohen-Aubart F, Rollins BJ, et al. Histiocytoses: emerging neoplasia behind inflammation. Lancet Oncol 2017; 18: e113–25. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Galindo C, Allen CE. Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood 2020; 135: 1319–31. - PubMed
-
- Goyal G, Heaney ML, Collin M, et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: consensus recommendations for evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment in the molecular era. Blood 2020; 135: 1929–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

