A randomized control trial of a child abuse mandated reporter training: Knowledge and attitudes
- PMID: 33901759
- PMCID: PMC8360385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2021.105033
A randomized control trial of a child abuse mandated reporter training: Knowledge and attitudes
Abstract
Background: Despite being well-positioned to identify maltreatment in the children that they provide care for and being legally required to report suspected child maltreatment, early childhood professionals (ECPs) make a limited proportion of reports to child protective services. It is critical to identify evidence-based interventions to improve the reporting practices of this group of mandated reporters allowing for the better protection of children from maltreatment.
Objective: The goal of the present study was to determine if iLookOut, an online child abuse identification and reporting training for ECPs, results in differential gains in knowledge and attitudes towards child abuse and its reporting among ECPs, as compared to an online standard training.
Participants and setting: Both interventions were completed online by participants recruited from licensed child care programs in Southern Maine from October 2017 to January 2020. Eligibility criteria included being at least 18 years of age, English-speaking, and working as paid or volunteer staff at a licensed child care program taking care of children 5 years of age or younger. Of the 1152 enrolled individuals, 1094 provided complete pre- and post-intervention data.
Methods: A randomized controlled trial comparing iLookOut with an online standard training.
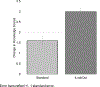
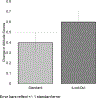
Results: ECPs who completed iLookOut significantly outperformed those who completed Standard mandated reporter training in terms of both knowledge (d=1.09 vs. 0.67) and attitudes (d=0.67 vs. 0.54) relative to pre-test scores.
Conclusions: iLookOut is a promising candidate for widespread use in meeting the need for evidence-based training on child abuse and its reporting.
Keywords: Abuse; Child maltreatment; Early childhood professionals; Mandated reporting; Neglect; Randomized controlled trial.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. (2020, August17). Ruran-Urban Commuting Area Codes. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes....
-
- Ajzen I, & Fishbein M (2005). The influence of attitudes on behaviour. In Albarracin D, Johnson B, & Zanna M (Eds.), The Handbook of Attitudes (pp. 173–221). Lawrence Erlbaum.
-
- Alvarez KM, Kenny MC, Donohue B, & Carpin KM (2004). Why are professionals failing to initiate mandated reports of child maltreatment, and are there any empirically based training programs to assist professionals in the reporting process? Aggression and Violent Behavior, 9(5), 563–578. 10.1016/j.avb.2003.07.001 - DOI
-
- United States Census Bureau. (2010). Urban and Rural: Maine. https://data.census.gov/cedsci/table?q=ruralmaine&g=0400000US23&tid=DECE...
-
- United States Census Bureau. (2018). QuickFacts: United States; Maine. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US,ME/INC910218
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical