Design and validation of a recognition instrument-the stroke aid for emergency scale-to predict large vessel occlusion stroke
- PMID: 33902003
- PMCID: PMC8202851
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202910
Design and validation of a recognition instrument-the stroke aid for emergency scale-to predict large vessel occlusion stroke
Abstract
Background and purpose: Rapidly recognizing patients with large-vessel occlusion stroke (LVOS) and transferring them to a center offering recanalization therapy is crucial of maximizing the benefits of early treatment. We therefore aimed to design an easy-to-use recognition instrument for identifying LVOS.
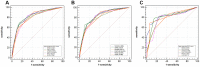
Methods: Prospective data were collected from emergency departments of 12 stroke-center hospitals in China during a 17-month study period. The Stroke Aid for Emergency (SAFE) scale is based on consciousness commands, facial palsy, gaze, and arm motor ability. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was used to obtain the area under the curve for the SAFE scale and previously established scales to predict LVOS.
Results: The SAFE scale could accurately predict LVOS at an accuracy rate comparable to that of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (c-statistics: 0.823 versus 0.831, p = 0.4798). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value for the SAFE scale were 0.6875, 0.8577, 0.6937, and 0.8542, respectively, with a cutoff point of 4. The SAFE scale also performed well in a subgroup analysis based on the patients' ages, occluded vessel locations, and the onset-to-door times.
Conclusions: The SAFE scale can accurately recognize LVOS at a rate comparable to those of other, similar scales.
Keywords: NIHSS; accuracy; endovascular therapy; large-vessel occlusion stroke; recognition instrument.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, Dávalos A, Majoie CB, van der Lugt A, de Miquel MA, Donnan GA, Roos YB, Bonafe A, et al., and HERMES collaborators. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. 2016; 387:1723–31. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00163-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pérez de la Ossa N, Carrera D, Gorchs M, Querol M, Millán M, Gomis M, Dorado L, López-Cancio E, Hernández-Pérez M, Chicharro V, Escalada X, Jiménez X, Dávalos A. Design and validation of a prehospital stroke scale to predict large arterial occlusion: the rapid arterial occlusion evaluation scale. Stroke. 2014; 45:87–91. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003071 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

