Free-breathing abdominal T1 mapping using an optimized MR fingerprinting sequence
- PMID: 33902155
- PMCID: PMC8218311
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.4531
Free-breathing abdominal T1 mapping using an optimized MR fingerprinting sequence
Abstract
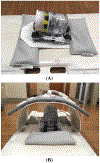
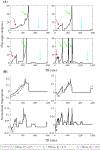
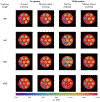
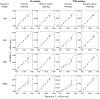
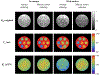
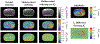
In this work, we propose a free-breathing magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) method that can be used to obtain B1+ -robust quantitative T1 maps of the abdomen in a clinically acceptable time. A three-dimensional MRF sequence with a radial stack-of-stars trajectory was implemented, and its k-space acquisition ordering was adjusted to improve motion-robustness in the context of MRF. The flip angle pattern was optimized using the Cramér-Rao Lower Bound, and the encoding efficiency of sequences with 300, 600, 900 and 1800 flip angles was evaluated. To validate the sequence, a movable multicompartment phantom was developed. Reference multiparametric maps were acquired under stationary conditions using a previously validated MRF method. Periodic motion of the phantom was used to investigate the motion-robustness of the proposed sequence. The best performing sequence length (600 flip angles) was used to image the abdomen during a free-breathing volunteer scan. When using a series of 600 or more flip angles, the estimated T1 values in the stationary phantom showed good agreement with the reference scan. Phantom experiments revealed that motion-related artifacts can appear in the quantitative maps and confirmed that a motion-robust k-space ordering is essential. The in vivo scan demonstrated that the proposed sequence can produce clean parameter maps while the subject breathes freely. Using this sequence, it is possible to generate B1+ -robust quantitative maps of T1 and B1+ next to M0 -weighted images under free-breathing conditions at a clinically usable resolution within 5 min.
Keywords: abdominal imaging, Cramér-Rao lower bound, magnetic resonance fingerprinting, quantitative imaging, respiratory motion.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Brown RW, Cheng Y-CN, Haacke EM, Thompson MR, Venkatesan R. Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Physical Principles and Sequence Design. 2nd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2014.
-
- Cheng H-LM, Stikov N, Ghugre NR, Wright GA. Practical medical applications of quantitative MR relaxometry. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 36(4):805–824. - PubMed
-
- Look DC, Locker DR. Time saving in measurement of NMR and EPR relaxation times. Rev Sci Instrum. 1970;41(2):250–251.
-
- Deoni SCL, Rutt BK, Peters TM. Rapid combined T1 and T2 mapping using gradient recalled acquisition in the steady state. Magn Reson Med. 2003; 49(3):515–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

