External Evaluation of Two Pediatric Population Pharmacokinetics Models of Oral Trimethoprim and Sulfamethoxazole
- PMID: 33903114
- PMCID: PMC8407045
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02149-20
External Evaluation of Two Pediatric Population Pharmacokinetics Models of Oral Trimethoprim and Sulfamethoxazole
Abstract
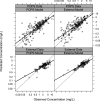
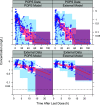
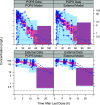
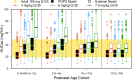
The antibiotic combination trimethoprim (TMP)-sulfamethoxazole (SMX) has a broad spectrum of activity and is used for the treatment of numerous infections, but pediatric pharmacokinetic (PK) data are limited. We previously published population PK (popPK) models of oral TMP-SMX in pediatric patients based on sparse opportunistically collected data (POPS study) (J. Autmizguine, C. Melloni, C. P. Hornik, S. Dallefeld, et al., Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62:e01813-17, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01813-17). We performed a separate PK study of oral TMP-SMX in infants and children with more-traditional PK sample collection and independently developed new popPK models of TMP-SMX using this external data set. The POPS data set and the external data set were each used to evaluate both popPK models. The external TMP model had a model and error structure identical to those of the POPS TMP model, with typical values for PK parameters within 20%. The external SMX model did not identify the covariates in the POPS SMX model as significant. The external popPK models predicted higher exposures to TMP (median overprediction of 0.13 mg/liter for the POPS data set and 0.061 mg/liter for the external data set) and SMX (median overprediction of 1.7 mg/liter and 0.90 mg/liter) than the POPS TMP (median underprediction of 0.016 mg/liter and 0.39 mg/liter) and SMX (median underprediction of 1.2 mg/liter and 14 mg/liter) models. Nonetheless, both models supported TMP-SMX dose increases in infants and young children for resistant pathogens with a MIC of 1 mg/liter, although the required dose increase based on the external model was lower. (The POPS and external studies have been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov under registration no. NCT01431326 and NCT02475876, respectively.).
Keywords: and sulfamethoxazole; pediatric; population pharmacokinetics; sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim.
Figures

References
-
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. 2009. Bactrim DS [package insert]. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=0138a156-859a-4....
-
- Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, Daum RS, Fridkin SK, Gorwitz RJ, Kaplan SL, Karchmer AW, Levine DP, Murray BE, J Rybak M, Talan DA, Chambers HF, Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2011. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children. Clin Infect Dis 52:e18–e55. 10.1093/cid/ciq146. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Klepser ME, Zhu Z, Nicolau DP, Banevicius MA, Belliveau PP, Ross JW, Broisman L, Quintiliani R, Nightingale CH. 1996. Oral absorption of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients with AIDS. Pharmacotherapy 16:656–662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 HD096435/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI143971/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN275201000003C/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM122741/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 FD006099/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- HHSN275201000003I/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R33 HL147833/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD090239/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R13 HD102136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD076676/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201300017C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201300017I/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD083465/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN275201700002C/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201500006C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U18 FD006298/FD/FDA HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

