The effects of interval training on peripheral brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33903670
- PMCID: PMC8076263
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-88496-x
The effects of interval training on peripheral brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
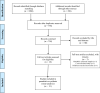
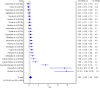
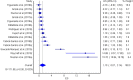
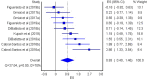
The aim of the current meta-analysis was to determine the effects of acute and chronic interval training (IT) on serum and plasma BDNF concentrations in healthy young adults. A literature search was performed using six databases until February 2020. The TESTEX scale was used to assess the quality of studies. Effect sizes (ES) were computed and two-tailed α values < 0.05 and non-overlapping 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were considered statistically significant. Heterogeneity, inconsistency (I2), and small-study effects using the Luis Furuya-Kanamori (LFK) index were examined. Fifteen studies (n = 277 participants, age = 24 ± 3 years) were included. The overall effects of IT on circulating BDNF concentrations were moderate and significant (ES = 0.62, 95% CI 0.00, 1.24, heterogeneous (p < 0.001), highly inconsistent (I2 = 90%), and with major asymmetry (LFK index = 2.76). The acute effect of IT on peripheral BDNF levels was large and significant (ES = 1.10, 95% CI 0.07, 2.14), heterogeneous (p < 0.001), highly inconsistent (I2 = 92%), and with major asymmetry (LFK index = 3.34). The chronic effect of IT on circulating BDNF was large and significant (ES = 0.93, 95% CI 0.40, 1.46), heterogeneous (p < 0.001), with moderate inconsistency (I2 = 70%), and minor asymmetry (LFK index = 1.21). Acute and chronic IT elicited a moderate increase in serum and plasma BDNF concentrations in a healthy young population.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effects of Acute and Chronic Exercise on Paraoxonase-1 (PON1): A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis.Res Q Exerc Sport. 2022 Mar;93(1):130-143. doi: 10.1080/02701367.2020.1812493. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2022. PMID: 32940564
-
Short-term high-Intensity interval training increases systemic brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in healthy women.Eur J Sport Sci. 2020 May;20(4):516-524. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2019.1650120. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020. PMID: 31386821 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of high intensity interval exercise on executive function and brain derived neurotrophic factor in healthy college aged males.Physiol Behav. 2018 Jul 1;191:116-122. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.04.018. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Physiol Behav. 2018. PMID: 29673858
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in substance use disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018 Dec 1;193:91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2018.08.036. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018. PMID: 30347311
-
Exercise Intensity and Recovery on Circulating Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020 May;52(5):1210-1217. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002242. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020. PMID: 31815833
Cited by
-
Neurophysiological mechanisms underlying cardiovascular adaptations to exercise: A narrative review.Physiol Rep. 2025 Jul;13(13):e70439. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70439. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40631359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Judo training program improves brain and muscle function and elevates the peripheral BDNF concentration among the elderly.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 16;12(1):13900. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17719-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35974038 Free PMC article.
-
The Effectiveness of Mindfulness in the Treatment of Methamphetamine Addiction Symptoms: Does Neuroplasticity Play a Role?Brain Sci. 2024 Mar 27;14(4):320. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14040320. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38671972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute effects of a single bout of high-intensity strength and endurance exercise on cognitive biomarkers in young adults and elderly men: a within-subjects crossover study.J Transl Med. 2025 Jun 19;23(1):685. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06685-y. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40537774 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Patterns, Serum BDNF and Fatty Acid Profiles in Physically Active Male Young Adults: A Cluster Analysis Study.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 15;16(24):4326. doi: 10.3390/nu16244326. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39770947 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

