GHS-R suppression in adipose tissues protects against obesity and insulin resistance by regulating adipose angiogenesis and fibrosis
- PMID: 33903722
- PMCID: PMC8238886
- DOI: 10.1038/s41366-021-00820-7
GHS-R suppression in adipose tissues protects against obesity and insulin resistance by regulating adipose angiogenesis and fibrosis
Abstract
Background/objectives: Ghrelin is an orexigenic hormone that increases food intake, adiposity, and insulin resistance through its receptor Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor (GHS-R). We previously showed that ghrelin/GHS-R signaling has important roles in regulation of energy homeostasis, and global deletion of GHS-R reduces obesity and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing thermogenesis. However, it is unknown whether GHS-R regulates thermogenic activation in adipose tissues directly.
Methods: We generated a novel adipose tissue-specific GHS-R deletion mouse model and characterized the mice under regular diet (RD) and high-fat diet (HFD) feeding. Body composition was measured by Echo MRI. Metabolic profiling was determined by indirect calorimetry. Response to environmental stress was assessed using a TH-8 temperature monitoring system. Insulin sensitivity was evaluated by glucose and insulin tolerance tests. Tissue histology was analyzed by hematoxylin/eosin and immunofluorescent staining. Expression of genes involved in thermogenesis, angiogenesis and fibrosis in adipose tissues were analyzed by real-time PCR.
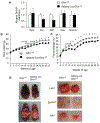
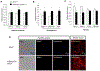
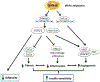
Results: Under RD feeding, adipose tissue-specific GHS-R deletion had little or no impact on metabolic parameters. However, under HFD feeding, adipose tissue-specific GHS-R deletion attenuated diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance, showing elevated physical activity and heat production. In addition, adipose tissue-specific GHS-R deletion increased expression of master adipose transcription regulator of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) γ1 and adipokines of adiponectin and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 21; and differentially modulated angiogenesis and fibrosis evident in both gene expression and histological analysis.
Conclusions: These results show that GHS-R has cell-autonomous effects in adipocytes, and suppression of GHS-R in adipose tissues protects against diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance by modulating adipose angiogenesis and fibrosis. These findings suggest adipose GHS-R may constitute a novel therapeutic target for treatment of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

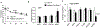
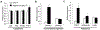
References
-
- Kursawe R, Caprio S, Giannini C, Narayan D, Lin A, D'Adamo E, et al. : Decreased transcription of ChREBP-alpha/beta isoforms in abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese adolescents with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes: associations with insulin resistance and hyperglycemia. Diabetes 2013, 62:837–844. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kozak LP, Koza RA, Anunciado-Koza R: Brown fat thermogenesis and body weight regulation in mice: relevance to humans. Int J Obes (Lond) 2010, 34 Suppl 1:S23–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

