Association of Vaginal Microbiota With Signs and Symptoms of the Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause Across Reproductive Stages
- PMID: 33903897
- PMCID: PMC8361365
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glab120
Association of Vaginal Microbiota With Signs and Symptoms of the Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause Across Reproductive Stages
Abstract
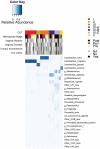
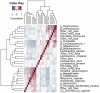
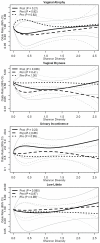
The genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) describes signs and symptoms resulting from effects of estrogen deficiency on the female genitourinary tract, including the vagina, labia, urethra, and bladder. Signs/symptoms associated with GSM may occur during any reproductive stage from multiple etiologies but are most common during menopause due to low estrogen. Vaginal microbiota, particularly Lactobacillus spp., are beneficial to the female genital tract; however, their abundance declines during menopause. We aimed to longitudinally assess vaginal microbiota characterized by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing and GSM-associated endpoints across reproductive stages. In a 2-year cohort study of 750 women aged 35-60 years at enrollment and 2 111 semiannual person-visits, low-Lactobacillus vaginal microbiota communities were observed at 21.2% (169/798), 22.9% (137/597), and 49.7% (356/716) of person-visits among pre-, peri-, and postmenopausal women, respectively (p < .001). Compared to communities that have high Gardnerella vaginalis relative abundance and diverse anaerobes, the following communities were associated with a lower covariate-adjusted odds of vaginal atrophy: L crispatus-dominated communities among postmenopausal women (odds ratio [OR] = 0.25; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.08, 0.81), L gasseri/L jensenii (OR = 0.21; 95% CI: 0.05, 0.94) and L iners (OR = 0.21; 95% CI: 0.05, 0.85) among perimenopausal women, and L iners-dominated communities (OR = 0.18; 95% CI: 0.04, 0.76) among premenopausal women. Postmenopausal women with L gasseri/L jensenii-dominated communities had the lowest odds of vaginal dryness (OR = 0.36; 95% CI: 0.12, 1.06) and low libido (OR = 0.28; 95% CI: 0.10, 0.74). Findings for urinary incontinence were inconsistent. Associations of vaginal microbiota with GSM signs/symptoms are most evident after menopause, suggesting an avenue for treatment and prevention.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; Low libido; Urinary incontinence; Vaginal atrophy; Vaginal microbiome.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Gerontological Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Portman DJ, Gass ML; Vulvovaginal Atrophy Terminology Consensus Conference Panel . Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: new terminology for vulvovaginal atrophy from the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and the North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2014;21:1063–1068. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000000329 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Łaniewski P, Owen KA, Khnanisho M, Brotman RM, Herbst-Kralovetz MM. Clinical and personal lubricants impact the growth of vaginal Lactobacillus species and colonization of vaginal epithelial cells: an in vitro study. Sex Transm Dis. 2021;48:63–70. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001272 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

