A prospective cohort study of rituximab in the treatment of refractory nephrotic syndrome
- PMID: 33905043
- PMCID: PMC8732927
- DOI: 10.1007/s11255-021-02860-4
A prospective cohort study of rituximab in the treatment of refractory nephrotic syndrome
Abstract
Objective: To explore the efficacy and safety of rituximab (RTX) in the treatment of autoimmune nephropathy manifested as refractory nephrotic syndrome (RNS).
Methods: A single-center prospective cohort study was conducted on RNS patients treated with RTX between March 2017 and December 2019. The subjects were divided into the primary nephropathy (PN) group and the secondary nephropathy (SN) group. Based on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) before RTX treatment, the SN group was then divided into the SN-1 group (eGFR ≥ 30 ml/min) and the SN-2 group (eGFR < 30 ml/min). Biochemical parameters and clinical data were recorded during follow-up.
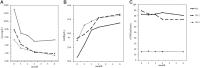
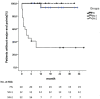
Results: Fifty-four patients were followed up for at least 6 months. The overall remission rates were 65%, 66.7%, 27.3% in the PN, SN-1, and SN-2 groups, respectively (P = 0.022). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a significant difference of the renal survival among the three subgroups (P < 0.001). Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that eGFR value before treatment was an independent predictor (HR 0.919, 95%CI 0.863-0.979) for renal survival. In terms of adverse events, infection accounted for 56.6%. The incidence of severe infection was 10%, 25% and 50% in PN group, SN-1 group and SN-2 group, respectively.
Conclusions: RTX may be a promising option in RNS patients with eGFR ≥ 30 ml/min/1.73m2. However, it has little effect on prognosis in patients with secondary RNS with eGFR < 30 ml/min/1.73m2, but with a high risk of severe infection.
Keywords: Albumin; Refractory nephrotic syndrome; Rituximab; Urine protein; eGFR.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Fervenza FC, Appel GB, Barbour SJ, Rovin BH, Lafayette RA, Aslam N, et al. Rituximab or cyclosporine in the treatment of membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;17(3):311–320. - PubMed
-
- Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K, et al. Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;384(9950):1273–1281. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60541-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous