Circulating IL-6, clusterin and irisin in obese subjects with different grades of obesity: association with insulin resistance and sexual dimorphism
- PMID: 33905632
- PMCID: PMC10065324
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000336
Circulating IL-6, clusterin and irisin in obese subjects with different grades of obesity: association with insulin resistance and sexual dimorphism
Abstract
Objective: There are discrepancies about the relationship of IL-6, clusterin and irisin with obesity and obesity associated insulin resistance and also about their sexual dimorphism. This study aimed at evaluating the circulating levels of IL-6, clusterin and irisin in obese subjects of both sexes who had different grades of obesity and examining their sexual dimorphism and their association with insulin resistance.
Methods: This study included 176 non-diabetic subjects of both sexes who were classified according to their sex into two groups; the male and the female groups. The male group (88 men) was classified according to BMI into; group 1 (22 lean men), group 2 (22 class I obese men), group 3 (22 class II obese men) and group 4 (22 class III obese men). The female group (88 women) was classified according to BMI exactly as the male group. Metabolic parameters, IL-6, clusterin, and irisin levels were measured. Data were analyzed by ANOVA test, post hoc Tukey's test and independent t-test. Pearson correlation was used to assess the association between variables.
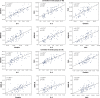
Results: In obese subjects of both sexes, circulating IL-6, clusterin and irisin levels were significantly elevated and positively correlated with HOMA-IR. Obese males showed significantly higher HOMA-IR, IL-6, clusterin and irisin levels than obese females.
Conclusion: Obesity in both sexes, especially in males was associated with high levels of IL-6, clusterin and irisin and worsened the metabolic pattern. Circulating IL-6, clusterin and irisin may represent possible therapeutic targets for insulin resistance in obese subjects.
Keywords: HOMA-IR; IL-6; clusterin; irisin; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relation of serum irisin level with metabolic and antropometric parameters in obese children.J Diabetes Complications. 2016 Nov-Dec;30(8):1560-1565. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.07.019. Epub 2016 Jul 28. J Diabetes Complications. 2016. PMID: 27539885
-
Irisin in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Metabolism. 2014 Feb;63(2):207-17. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.013. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24140091
-
Circulating serum irisin levels in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus.IUBMB Life. 2016 Jul;68(7):544-56. doi: 10.1002/iub.1511. Epub 2016 May 24. IUBMB Life. 2016. PMID: 27220658
-
The Usefulness of Diagnostic Panels Based on Circulating Adipocytokines/Regulatory Peptides, Renal Function Tests, Insulin Resistance Indicators and Lipid-Carbohydrate Metabolism Parameters in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Obesity.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 9;10(9):1304. doi: 10.3390/biom10091304. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32917052 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Circulating Irisin with Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress in Obese Women.Horm Metab Res. 2016 Sep;48(10):653-657. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-116155. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Horm Metab Res. 2016. PMID: 27632149
Cited by
-
Impact of Large-Volume Liposuction on Inflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-6 Levels: A Cross-Sectional Study.Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2025 Apr 12;7:ojaf021. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojaf021. eCollection 2025. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2025. PMID: 40351557 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Exercise Interventions on Irisin and Interleukin-6 Concentrations and Indicators of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Males with Metabolic Syndrome.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 3;12(1):369. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010369. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36615169 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the function of clusterin in the progression of diabetic kidney disease.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 14;16:1573654. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1573654. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40438587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of body composition on patient prognosis after SARS-Cov-2 infection.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 28;18(7):e0289206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289206. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37506083 Free PMC article.
-
Relation of serum irisin levels with adiposity, components of metabolic syndrome and carotid intima media thickness in prepubertal children with obesity: a cross-sectional study.Endocrine. 2025 Mar;87(3):1031-1040. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-04139-x. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 39725768
References
-
- Moreno-Navarrete JM, Ortega F, Serrano M, Guerra E, Pardo G, Tinahones F, et al. Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(4):E769–E778. - PubMed
-
- Eder K, Baffy N, Falus A, Fulop AK. The major inflammatory mediator interleukin-6 and obesity. Inflamm Res. 2009;58(11):727–736. - PubMed
-
- Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA. Muscle as an endocrine organ: focus on muscle-derived interleukin-6. Physiol. Rev. 2008;88:1379–1406. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous