High-throughput functional variant screens via in vivo production of single-stranded DNA
- PMID: 33906944
- PMCID: PMC8106316
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2018181118
High-throughput functional variant screens via in vivo production of single-stranded DNA
Abstract
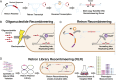
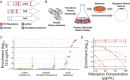
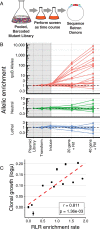
Creating and characterizing individual genetic variants remains limited in scale, compared to the tremendous variation both existing in nature and envisioned by genome engineers. Here we introduce retron library recombineering (RLR), a methodology for high-throughput functional screens that surpasses the scale and specificity of CRISPR-Cas methods. We use the targeted reverse-transcription activity of retrons to produce single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) in vivo, incorporating edits at >90% efficiency and enabling multiplexed applications. RLR simultaneously introduces many genomic variants, producing pooled and barcoded variant libraries addressable by targeted deep sequencing. We use RLR for pooled phenotyping of synthesized antibiotic resistance alleles, demonstrating quantitative measurement of relative growth rates. We also perform RLR using the sheared genomic DNA of an evolved bacterium, experimentally querying millions of sequences for causal variants, demonstrating that RLR is uniquely suited to utilize large pools of natural variation. Using ssDNA produced in vivo for pooled experiments presents avenues for exploring variation across the genome.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; functional genomics; genetic engineering; retron; synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: M.G.S., T.M.W., F.F., T.K.L., S.L.S., and G.M.C. have filed patent applications based on related work. T.K.L. is a cofounder of Senti Biosciences, Synlogic, Engine Biosciences, Tango Therapeutics, Corvium, BiomX, and Eligo Biosciences, in which he has related financial interests. T.K.L. also holds financial interests in nest.bio, Ampliphi, IndieBio, MedicusTek, Quark Biosciences, and Personal Genomics. G.M.C. is a cofounder of companies in which he has related financial interests: EnEvolv and 64-x. For a complete list of G.M.C.’s financial interests, see https://arep.med.harvard.edu/gmc/tech.html.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Retron Library Recombineering: Next Powerful Tool for Genome Editing after CRISPR/Cas.ACS Synth Biol. 2024 Apr 19;13(4):1019-1025. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00667. Epub 2024 Mar 13. ACS Synth Biol. 2024. PMID: 38480006 Review.
-
Coupling ssDNA recombineering with CRISPR-Cas9 for Escherichia coli DnaG mutations.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Apr;103(8):3559-3570. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09744-9. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30879090
-
Simultaneous multi-site editing of individual genomes using retron arrays.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Nov;20(11):1482-1492. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01665-7. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38982310 Free PMC article.
-
Pooled clone collections by multiplexed CRISPR-Cas12a-assisted gene tagging in yeast.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 4;10(1):2960. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10816-7. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31273196 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellularly synthesized ssDNA for continuous genome engineering.Trends Biotechnol. 2025 Jun;43(6):1356-1370. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2024.10.011. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Trends Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39537537 Review.
Cited by
-
High-throughput colocalization pipeline quantifies efficacy of mitochondrial targeting signals across different protein types.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 3:2023.04.03.535288. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.03.535288. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Aug 18;12(8):2498-2504. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00349. PMID: 37066162 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Reducing competition between msd and genomic DNA improves retron editing efficiency.EMBO Rep. 2024 Dec;25(12):5316-5330. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00311-6. Epub 2024 Nov 5. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 39501049 Free PMC article.
-
Disassembly activates Retron-Septu for antiphage defense.Science. 2025 Jun 12:eadv3344. doi: 10.1126/science.adv3344. Online ahead of print. Science. 2025. PMID: 40504952 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma contains ultrashort single-stranded DNA in addition to nucleosomal cell-free DNA.iScience. 2022 Jun 8;25(7):104554. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104554. eCollection 2022 Jul 15. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35800774 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structures of Escherichia coli Ec86 retron complexes reveal architecture and defence mechanism.Nat Microbiol. 2022 Sep;7(9):1480-1489. doi: 10.1038/s41564-022-01197-7. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Nat Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35982312
References
-
- Richardson S. M., et al. , Design of a synthetic yeast genome. Science 355, 1040–1044 (2017). - PubMed
-
- C. A. Hutchison, 3rd, et al. , Design and synthesis of a minimal bacterial genome. Science 351, aad6253 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Warner J. R., Reeder P. J., Karimpour-Fard A., Woodruff L. B. A., Gill R. T., Rapid profiling of a microbial genome using mixtures of barcoded oligonucleotides. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 856–862 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

