Localization of the hydrogen sulfide and oxytocin systems at the depth of the sulci in a porcine model of acute subdural hematoma
- PMID: 33907009
- PMCID: PMC8374554
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.313018
Localization of the hydrogen sulfide and oxytocin systems at the depth of the sulci in a porcine model of acute subdural hematoma
Abstract
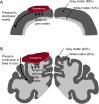
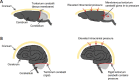
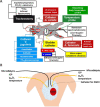
In the porcine model discussed in this review, the acute subdural hematoma was induced by subdural injection of autologous blood over the left parietal cortex, which led to a transient elevation of the intracerebral pressure, measured by bilateral neuromonitoring. The hematoma-induced brain injury was associated with albumin extravasation, oxidative stress, reactive astrogliosis and microglial activation in the ipsilateral hemisphere. Further proteins and injury markers were validated to be used for immunohistochemistry of porcine brain tissue. The cerebral expression patterns of oxytocin, oxytocin receptor, cystathionine-γ-lyase and cystathionine-β-synthase were particularly interesting: these four proteins all co-localized at the base of the sulci, where pressure-induced brain injury elicits maximum stress. In this context, the pig is a very relevant translational model in contrast to the rodent brain. The structure of the porcine brain is very similar to the human: the presence of gyri and sulci (gyrencephalic brain), white matter to grey matter proportion and tentorium cerebelli. Thus, pressure-induced injury in the porcine brain, unlike in the rodent brain, is reflective of the human pathophysiology.
Keywords: animal modeling; brain edema; cystathionine-β-synthase; cystathionine-γ-lyase; gyrencephalic brain; immunohistochemistry; intensive care unit; large animal model; neuromonitoring; oxytocin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brain Histology and Immunohistochemistry After Resuscitation From Hemorrhagic Shock in Swine With Pre-Existing Atherosclerosis and Sodium Thiosulfate (Na2S2O3) Treatment.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 30;9:925433. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.925433. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35847799 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Targeted Hyperoxemia on Brain Immunohistochemistry after Long-Term, Resuscitated Porcine Acute Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhagic Shock.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 14;25(12):6574. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126574. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928283 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral Immunohistochemical Characterization of the H2S and the Oxytocin Systems in a Porcine Model of Acute Subdural Hematoma.Front Neurol. 2020 Jul 7;11:649. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00649. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32754111 Free PMC article.
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in secondary neuronal injury.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24239876 Review.
-
Benign meningioma manifesting with acute subdural hematoma and cerebral edema: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2021 Jun 29;15(1):335. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02935-x. J Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34187580 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Histology and Immunohistochemistry After Resuscitation From Hemorrhagic Shock in Swine With Pre-Existing Atherosclerosis and Sodium Thiosulfate (Na2S2O3) Treatment.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 30;9:925433. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.925433. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35847799 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Targeted Hyperoxemia on Brain Immunohistochemistry after Long-Term, Resuscitated Porcine Acute Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhagic Shock.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 14;25(12):6574. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126574. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928283 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Connection of Psychological Stress and Polytrauma under Intensive Care: The Role of Oxytocin and Hydrogen Sulfide.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 25;22(17):9192. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179192. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H2S and Oxytocin Systems in Early Life Stress and Cardiovascular Disease.J Clin Med. 2021 Aug 6;10(16):3484. doi: 10.3390/jcm10163484. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34441780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessandri B, Heimann A, Filippi R, Kopacz L, Kempski O. Moderate controlled cortical contusion in pigs: effects on multi-parametric neuromonitoring and clinical relevance. J Neurotrauma. 2003;20:1293–1305. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RW, Brown CJ, Blumbergs PC, McLean AJ, Jones NR. Impact mechanics and axonal injury in a sheep model. J Neurotrauma. 2003;20:961–974. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

