FtsZ treadmilling is essential for Z-ring condensation and septal constriction initiation in Bacillus subtilis cell division
- PMID: 33907196
- PMCID: PMC8079713
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22526-0
FtsZ treadmilling is essential for Z-ring condensation and septal constriction initiation in Bacillus subtilis cell division
Abstract
Despite the central role of division in bacterial physiology, how division proteins work together as a nanoscale machine to divide the cell remains poorly understood. Cell division by cell wall synthesis proteins is guided by the cytoskeleton protein FtsZ, which assembles at mid-cell as a dense Z-ring formed of treadmilling filaments. However, although FtsZ treadmilling is essential for cell division, the function of FtsZ treadmilling remains unclear. Here, we systematically resolve the function of FtsZ treadmilling across each stage of division in the Gram-positive model organism Bacillus subtilis using a combination of nanofabrication, advanced microscopy, and microfluidics to measure the division-protein dynamics in live cells with ultrahigh sensitivity. We find that FtsZ treadmilling has two essential functions: mediating condensation of diffuse FtsZ filaments into a dense Z-ring, and initiating constriction by guiding septal cell wall synthesis. After constriction initiation, FtsZ treadmilling has a dispensable function in accelerating septal constriction rate. Our results show that FtsZ treadmilling is critical for assembling and initiating the bacterial cell division machine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
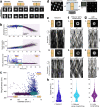
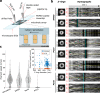


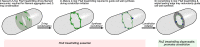
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

