Extracellular Vesicles from Akkermansia muciniphila Elicit Antitumor Immunity Against Prostate Cancer via Modulation of CD8+ T Cells and Macrophages
- PMID: 33907401
- PMCID: PMC8068512
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S304515
Extracellular Vesicles from Akkermansia muciniphila Elicit Antitumor Immunity Against Prostate Cancer via Modulation of CD8+ T Cells and Macrophages
Abstract
Purpose: Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the most common malignancies in males. Despite the success of immunotherapy in many malignant cancers, strategies are still needed to improve therapeutic efficacy in PCa. This study aimed to investigate the effects of Akkermansia muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles (Akk-EVs) on PCa and elucidate the underlying immune-related mechanism.
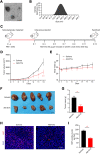
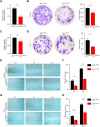
Methods: Akk-EVs were isolated by ultracentrifugation and intravenously injected to treat syngeneic PCa-bearing immune-competent mice. Immunophenotypic changes in immune cells, such as cytotoxic T lymphocytes and macrophages, were measured via flow cytometry analysis. Histological examination was used to detect morphological changes in major organs after Akk-EVs treatments. In vitro, flow cytometry was performed to confirm the effects of Akk-EVs on the activation of CD8+ T cells. Quantitative PCR and immunofluorescence staining were carried out to test the impact of Akk-EVs on macrophage polarization. Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) analysis, colony formation assays, and scratch wound healing assays were conducted to assess the effects of Akk-EVs-treated macrophages on the proliferation and invasion of PCa cells. CCK-8 assays also confirmed the impact of Akk-EVs on the viability of normal cells.
Results: Intravenous injection of Akk-EVs in immune-competent mice reduced the tumor burden of PCa without inducing obvious toxicity in normal tissues. This treatment elevated the proportion of granzyme B-positive (GZMB+) and interferon γ-positive (IFN-γ+) lymphocytes in CD8+ T cells and caused macrophage recruitment, with increased tumor-killing M1 macrophages and decreased immunosuppressive M2 macrophages. In vitro, Akk-EVs increased the number of GZMB+CD8+ and IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells and M1-like macrophages. In addition, conditioned medium from Akk-EVs-treated macrophages suppressed the proliferation and invasion of prostate cells. Furthermore, the effective dose of Akk-EVs was well-tolerated in normal cells.
Conclusion: Our study revealed the promising prospects of Akk-EVs as an efficient and biocompatible immunotherapeutic agent for PCa treatment.
Keywords: Akkermansia muciniphila; cytotoxic T lymphocytes; extracellular vesicles; immunotherapy; macrophages; prostate cancer.
© 2021 Luo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

