A Remarkable and Durable Response to Sintilimab and Anlotinib in the First-Line Treatment of an Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma without Targetable Genomic Alterations: A Case Report
- PMID: 33907417
- PMCID: PMC8068508
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S305196
A Remarkable and Durable Response to Sintilimab and Anlotinib in the First-Line Treatment of an Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma without Targetable Genomic Alterations: A Case Report
Abstract
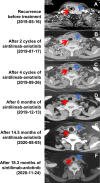
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) is a rare and highly aggressive fatal tumor. Most ATC patients using traditional surgery or radio-chemotherapy have poor prognosis and experience recurrence in a very short time. There is no optimal therapy for ATC, and the median survival time is about 5 months. We report a 67-year-old ATC patient, who experienced rapid local recurrence after radical thyroidectomy. The resected tumor tissue was sent for immunohistochemistry analysis and targeted next-generation sequencing. The results indicated high PD-L1 expression, a tumor mutation burden of 0.48 muts/Mb, microsatellite stable, and somatic mutations of TERT promoter, EIF1AX, NRAS and TP53. However, none of the mutations indicated corresponding target therapy. An immediate operation was unsuitable because of rapid recurrence after surgery. The patient was also not in a condition to tolerate chemotherapy. Based on the high expression of PD-L1, an optimum strategy was used, combining immunotherapeutic agent, sintilimab, with an anti-angiogenesis drug, anlotinib. The patient obtained remarkable tumor shrinkage and an 18.3-month-sustained remission period. This is an effective case of using immunotherapy and anti-angiogenesis agent in the first-line treatment of ATC. It demonstrates a feasible and novel therapeutic option for future treatment of ATC patients.
Keywords: NRAS mutation; PD-1 inhibitor; TERT promoter mutations; TP53 mutations; anaplastic thyroid carcinoma; anti-angiogenesis drug; next-generation sequencing.
© 2021 Gui et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

