Depletion of hsa_circ_0000144 Suppresses Oxaliplatin Resistance of Gastric Cancer Cells by Regulating miR-502-5p/ADAM9 Axis
- PMID: 33907420
- PMCID: PMC8068497
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S281238
Depletion of hsa_circ_0000144 Suppresses Oxaliplatin Resistance of Gastric Cancer Cells by Regulating miR-502-5p/ADAM9 Axis
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been disclosed to exert important roles in human cancers, including gastric cancer (GC). CircRNA hsa_circ_0000144 was identified as an oncogene in GC development. The aim of our study was to explore the role of hsa_circ_0000144 in oxaliplatin (OXA) resistance of GC.
Methods: Expression levels of hsa_circ_0000144, microRNA-502-5p (miR-502-5p) and A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 9 (ADAM9) were examined by quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) or Western blot assay. The OXA resistance of GC cells was evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Colony formation assay was performed to assess the colony formation capacity. Cell apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry and caspase 3 activity. And cell migration and invasion were detected by Transwell assay. Target association between miR-502-5p and hsa_circ_0000144 or ADAM9 was demonstrated by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay. Moreover, role of hsa_circ_0000144 in vivo was analyzed by xenograft tumor assay.
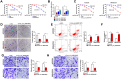
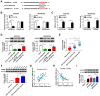
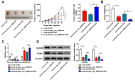
Results: Hsa_circ_0000144 and ADAM9 were highly expressed, while miR-502-5p was downregulated in OXA-resistant GC tissues and cells. Depletion of hsa_circ_0000144 could inhibit OXA resistance, proliferation and metastasis in OXA-resistant GC cells, which was attenuated by miR-502-5p inhibition. Hsa_circ_0000144 sponged miR-502-5p to positively regulate ADAM9 expression. MiR-502-5p suppressed OXA resistance, proliferation and metastasis in OXA-resistant GC cells by targeting ADAM9. Hsa_circ_0000144 knockdown could hamper tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion: Hsa_circ_0000144 exerted inhibitory effects on OXA resistance, proliferation and metastasis of OXA-resistant GC cells by regulating miR-502-5p/ADAM9 axis, at least in part.
Keywords: ADAM9; GC; OXA resistance; OXA-resistant GC cells; hsa_circ_0000144; miR-502-5p.
© 2021 Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or non-financial conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Circular RNA circLRCH3 promotes oxaliplatin resistance in gastric cancer through the modulation of the miR-383-5p/FGF7 axis.Histol Histopathol. 2023 Jun;38(6):647-658. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-506. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Histol Histopathol. 2023. PMID: 35920365
-
Knockdown of circ-ADAM9 inhibits malignant phenotype and enhances radiosensitivity in breast cancer cells via acting as a sponge for miR-383-5p.Strahlenther Onkol. 2023 Jan;199(1):78-89. doi: 10.1007/s00066-022-02006-0. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Strahlenther Onkol. 2023. PMID: 36205752
-
Depletion of Circular RNA circ_CORO1C Suppresses Gastric Cancer Development by Modulating miR-138-5p/KLF12 Axis.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 May 11;13:3789-3801. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S290629. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34007212 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa_circ_0000231 knockdown inhibits the glycolysis and progression of colorectal cancer cells by regulating miR-502-5p/MYO6 axis.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 Sep 29;18(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-02033-0. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32993655 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the oncogenic and tumor-suppressive roles of Circ-ADAM9 in cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Apr;256:155257. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155257. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38537524 Review.
Cited by
-
Hsa_circ_0041150 serves as a novel biomarker for monitoring chemotherapy resistance in small cell lung cancer patients treated with a first-line chemotherapy regimen.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(17):15365-15382. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05317-6. Epub 2023 Aug 28. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37639013 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA SOX5 promotes the proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis of the hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting miR-502-5p/synoviolin 1 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):3362-3370. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2029110. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35048790 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA: A new class of targets for gastric cancer drug resistance therapy.Pathol Oncol Res. 2023 Mar 30;29:1611033. doi: 10.3389/pore.2023.1611033. eCollection 2023. Pathol Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 37065861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of circular RNAs in gastric cancer metastasis and drug resistance.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jul 11;41(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02432-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35821160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircWalk: a novel approach to predict CircRNA-disease association based on heterogeneous network representation learning.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Aug 11;23(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04883-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35953785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Compare D, Rocco A, Nardone G. Risk factors in gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010;14(4):302–308. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

