Inflammatory stress in SARS-COV-2 associated Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 33907513
- PMCID: PMC8071761
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.58791
Inflammatory stress in SARS-COV-2 associated Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
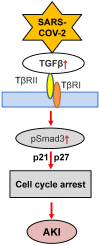
Increasing clinical evidence shows that acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and severe complication in critically ill COVID-19 patients. The older age, the severity of COVID-19 infection, the ethnicity, and the history of smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease are the risk factor for AKI in COVID-19 patients. Of them, inflammation may be a key player in the pathogenesis of AKI in patients with COVID-19. It is highly possible that SARS-COV-2 infection may trigger the activation of multiple inflammatory pathways including angiotensin II, cytokine storm such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), TGF-β signaling, complement activation, and lung-kidney crosstalk to cause AKI. Thus, treatments by targeting these inflammatory molecules and pathways with a monoclonal antibody against IL-6 (Tocilizumab), C3 inhibitor AMY-101, anti-C5 antibody, anti-TGF-β OT-101, and the use of CRRT in critically ill patients may represent as novel and specific therapies for AKI in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: AKI; COVID-19; cytokines; inflammation; mechanisms.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Be aware of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with COVID-19.Pediatr Nephrol. 2021 Jan;36(1):163-169. doi: 10.1007/s00467-020-04715-z. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 32844290 Free PMC article.
-
[An overview on acute kidney injury in COVID-19].G Ital Nefrol. 2021 Jun 24;38(3):2021-vol3. G Ital Nefrol. 2021. PMID: 34169691 Review. Italian.
-
Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Replacement Therapy in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: Risk Factors and Outcomes: A Single-Center Experience in Brazil.Blood Purif. 2021;50(4-5):520-530. doi: 10.1159/000513425. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Blood Purif. 2021. PMID: 33341806 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy for a Patient with Severe COVID-19.Blood Purif. 2021;50(1):129-131. doi: 10.1159/000508062. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Blood Purif. 2021. PMID: 32526746 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 28;22(15):8081. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158081. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Jeopardy of COVID-19: Rechecking the Perks of Phytotherapeutic Interventions.Molecules. 2021 Nov 10;26(22):6783. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226783. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34833873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors associated with acute kidney injury (AKI) and mortality in COVID-19 patients in a Sub-Saharan African intensive care unit: a single-center prospective study.Ren Fail. 2023;45(2):2263583. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2263583. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37870858 Free PMC article.
-
Role of C-Reactive Protein in Kidney Diseases.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;9(2):73-81. doi: 10.1159/000528693. eCollection 2023 Apr. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2022. PMID: 37065607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smad3 Signatures in Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Mar 28;18(7):2795-2806. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.71595. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35541902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term effects of Omicron BA.2 breakthrough infection on immunity-metabolism balance: a 6-month prospective study.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 19;15(1):2444. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46692-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38503738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323:1239–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

