Emerging materials for the electrochemical detection of COVID-19
- PMID: 33907536
- PMCID: PMC8062413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115289
Emerging materials for the electrochemical detection of COVID-19
Abstract
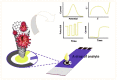
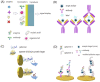
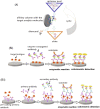
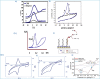
The SARS-CoV-2 virus is still causing a dramatic loss of human lives worldwide, constituting an unprecedented challenge for the society, public health and economy, to overcome. The up-to-date diagnostic tests, PCR, antibody ELISA and Rapid Antigen, require special equipment, hours of analysis and special staff. For this reason, many research groups have focused recently on the design and development of electrochemical biosensors for the SARS-CoV-2 detection, indicating that they can play a significant role in controlling COVID disease. In this review we thoroughly discuss the transducer electrode nanomaterials investigated in order to improve the sensitivity, specificity and response time of the as-developed SARS-CoV-2 electrochemical biosensors. Particularly, we mainly focus on the results appeard on Au-based and carbon or graphene-based electrodes, which are the main material groups recently investigated worldwidely. Additionally, the adopted electrochemical detection techniques are also discussed, highlighting their pros and cos. The nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors could enable a fast, accurate and without special cost, virus detection. However, further research is required in terms of new nanomaterials and synthesis strategies in order the SARS-CoV-2 electrochemical biosensors to be commercialized.
Keywords: Au-based nanomaterials; COVID-19 control; Carbon-based nanomaterials; Electrochemical biosensors; Electrochemical detection; SARS-CoV-2 virus detection.
© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.-L., Wang X.-G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.-R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.-L., Chen H.-D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.-D., Liu M.-Q., Chen Y., Shen X.-R., Wang X., Zheng X.-S., Zhao K., Chen Q.-J., Deng F., Liu L.-L., Yan B., Zhan F.-X., Wang Y.-Y., Xiao G.-F., Shi Z.-L. Nature. 2020;579:270–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yuan X., Yang C., He Q., Chen J., Yu D., Li J., Zhai S., Qin Z., Du K., Chu Z., Qin P. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020;6:1998–2016. - PubMed
-
- FDA: U.S Food & Drug, A Closer Look at Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Diagnostic Testing. 2020
-
- Udugama B., Kadhiresan P., Kozlowski H.N., Malekjahani A., Osborne M., Li V.Y.C., Chen H., Mubareka S., Gubbay J.B., Chan W.C.W. ACS Nano. 2020;14:3822–3835. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
