Long non-coding RNA SNHG17 enhances the aggressiveness of C4-2 human prostate cancer cells in association with β-catenin signaling
- PMID: 33907582
- PMCID: PMC8063240
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2021.12733
Long non-coding RNA SNHG17 enhances the aggressiveness of C4-2 human prostate cancer cells in association with β-catenin signaling
Abstract
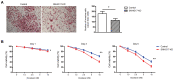
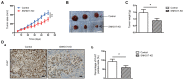
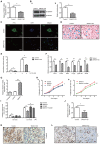
Long non-coding (lnc) RNAs have emerged as important regulators of cancer development and progression. Several lncRNAs have been reported to be associated with prostate cancer (PCa); however, the involvement of lncRNA SNHG17 in PCa remains unclear. In the present study, the mRNA expression level of SNHG17 in 58 pairs of PCa tumor samples and adjacent non-tumor tissues, as well as in PCa tumor cell lines was analyzed. The regulatory effect of SNHG17 on the oncogenic phenotypes of the C4-2 tumor cell line was also investigated. The clinicopathological analysis revealed that SNHG17 mRNA expression level was increased in the PCa tumor samples, and its high expression levels were associated with poor patient outcomes, indicating that SNHG17 may act as a biomarker for the prognosis of PCa. SNHG17 mRNA expression level was also increased in different PCa tumor cell lines. Functionally, SNHG17 increased C4-2 tumor cell growth and aggressiveness by stimulating tumor cell proliferation, survival, invasion and resistance to chemotherapy. Furthermore, SNHG17 promoted in vivo tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model. Notably, the SNHG17-induced in vitro and in vivo oncogenic effects were associated with activation of the β-catenin pathway. The results from the present study revealed that lncRNA SNHG17 could be an important regulator in the oncogenic properties of human PCa and may; therefore, represent a potential PCa therapeutic target.
Keywords: SNHG17; Wnt; lncRNA; prostate cancer.
Copyright: © Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
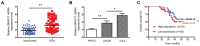

References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, Dicker DJ, Chimed-Orchir O, Dandona R, et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:524–548. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
