Space Flight-Associated Neuroocular Syndrome, Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension, and Pseudotumor Cerebri: Phenotypic Descriptions, Pathogenesis, and Hydrodynamics
- PMID: 33907644
- PMCID: PMC8067672
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14103
Space Flight-Associated Neuroocular Syndrome, Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension, and Pseudotumor Cerebri: Phenotypic Descriptions, Pathogenesis, and Hydrodynamics
Abstract
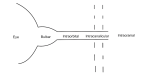
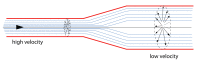
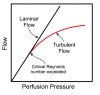
Recent data from astronauts who have returned to Earth from a long-duration space flight have unequivocally distinguished spaceflight-associated neuro-ocular syndrome (SANS) from idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) and pseudotumor cerebri (PTC). We review the semiology and pathogenesis of these three entities, noting that optic disc edema is what unites them, and this where the similarities between SANS and IIH/PTC end. We distinguish between PTC and IIH and between SANS and IIH/PTC and review the medical and surgical therapy of IIH/PTC. The key to understanding the phenomenon of optic disc edema is the geometry of the optic nerve sheath, which is a simulacrum of an inverted Venturi tube. This allows us to theoretically study the hydrodynamics of the optic nerve sheath by applying simple physical laws, including the Venturi effect, Poiseuille's law, and Reynold's number, and we speculate on nature's design and the correlation of form and function in understanding how cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates in the optic nerve sheath as it approaches the optic nerve head. Recent spectacular data on the histology of the blood nerve-barrier of the optic nerve disc and the glymphatic system of the optic nerve sheath will also help us understand the development of optic disc edema due to the microgravity-induced cephalad shift of CSF in SANS. We will explore the role of the sodium/potassium adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) pump on choroid plexus epithelial cells and the aquaporin-4 water receptors located on astrocyte end-feet and their complex interactions with the tetracyclines, mineralocorticoids, and therapeutic agents with carbonic anhydrase activity. We also adumbrate the complex interactions between obesity, vitamin A, and 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and how the aquaporin-4 receptor relates to these interactions.
Keywords: idiopathic intracranial hypertension (iih); microgravity.
Copyright © 2021, Kesserwani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Intracranial pressure without brain tumor: diagnosis and treatment. Dandy WE. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1390605/ Ann Surg. 1937;106:492–513. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Wall M, Corbett JJ. Neurology. 2014;83:198–199. - PubMed
-
- Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Friedman DI, Liu GT, Digre KB. Neurology. 2013;81:1159–1165. - PubMed
-
- Benign intracranial hypertension. Weisberg LA. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975;54:197–207. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
