DNAJC12 promotes lung cancer growth by regulating the activation of β‑catenin
- PMID: 33907820
- PMCID: PMC8057298
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4938
DNAJC12 promotes lung cancer growth by regulating the activation of β‑catenin
Abstract
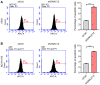
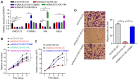
Lung cancer has become the leading cause of cancer‑associated mortality worldwide. However, the underlying mechanisms of lung cancer remain poorly understood. DnaJ heat shock protein family (HSP40) member C12 (DNAJC12) is a type III member belonging to the HSP40/DNAJ family. The role of DNAJC12 in numerous types of cancer has been previously reported; however, the effect of DNAJC12 in lung cancer remains unknown. The results of the present study indicated that DNAJC12 may be involved in lung cancer proliferation and migration by regulating the β‑catenin signaling pathway. Data generated in the present study and from The Cancer Genome Atlas revealed that the DNAJC12 expression levels were significantly upregulated in lung cancer tissues compared with non‑cancer lung tissues. The expression of DNAJC12 was subsequently knocked down in A549 and NCI‑H1975 lung cancer cells using lentiviral transfections and further experiments demonstrated that the knockdown of DNAJC12 inhibited the proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. The results of flow cytometric assays also revealed that the knockdown of DNAJC12 induced the apoptosis of lung cancer cells. In addition, the effects of DNAJC12 knockdown on the in vivo growth of lung cancer cells were observed. Signaling pathway analysis revealed that the knockdown of DNAJC12 expression suppressed the phosphorylation of p65 NF‑κB, downregulated the expression levels and inhibited the subsequent activation of β‑catenin, and downregulated the expression levels of vimentin. Rescue experiments demonstrated that the overexpression of β‑catenin, but not that of NF‑κB or vimentin, reversed the effects of DNAJC12 knockdown on the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells. On the whole, the findings of the present study suggest that DNAJC12 may play a crucial role in lung cancer tumorigenesis by regulating the expression and activation of β‑catenin. Therefore, DNAJC12 may represent a novel target for the treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member C12; apoptosis; lung cancer; migration; proliferation; β‑catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

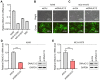
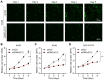
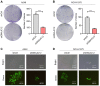

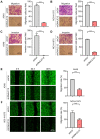

Similar articles
-
IL‑21/IL‑21R inhibit tumor growth and invasion in non‑small cell lung cancer cells via suppressing Wnt/β‑catenin signaling and PD‑L1 expression.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Nov;44(5):1697-1706. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4354. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31573051 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO3a inhibits nephroblastoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and induces apoptosis through downregulating the Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Nov;24(5):796. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12436. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34515328 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 promotes tumor growth and progression by activating WIP and β-catenin signaling pathways and predicts poor prognosis in lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 6;11(7):506. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2701-z. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32632098 Free PMC article.
-
Long non‑coding RNA LINC01748 exerts carcinogenic effects in non‑small cell lung cancer cell lines by regulating the microRNA‑520a‑5p/HMGA1 axis.Int J Mol Med. 2022 Feb;49(2):22. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5077. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34970695 Free PMC article.
-
DNAJC12 in Monoamine Metabolism, Neurodevelopment, and Neurodegeneration.Mov Disord. 2024 Feb;39(2):249-258. doi: 10.1002/mds.29677. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Mov Disord. 2024. PMID: 38014588 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the molecular interface of gene expression dynamics and prostate cancer susceptibility in response to HBCD exposure.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025 Feb 3;14(1):tfaf016. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaf016. eCollection 2025 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025. PMID: 39906184
-
Silencing FGL1 promotes prostate cancer cell apoptosis and inhibits EMT progression.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 6;15(1):19886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04717-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40481127 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of p53 and Cancer Signaling by Heat Shock Protein 40/J-Domain Protein Family Members.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 16;22(24):13527. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413527. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Personalized drug screening in patient-derived organoids of biliary tract cancer and its clinical application.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Nov 21;4(11):101277. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101277. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 37944531 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of DNAJC12 Expression Predicts Worse Survival for ER-Positive Breast Cancer Patients.Biomark Insights. 2025 Feb 24;20:11772719251323095. doi: 10.1177/11772719251323095. eCollection 2025. Biomark Insights. 2025. PMID: 40008192 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

