The synaptic inputs and thalamic projections of two classes of layer 6 corticothalamic neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of the mouse
- PMID: 33908623
- PMCID: PMC8551307
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.25163
The synaptic inputs and thalamic projections of two classes of layer 6 corticothalamic neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of the mouse
Erratum in
-
Erratum.J Comp Neurol. 2022 May;530(7):1126. doi: 10.1002/cne.25315. J Comp Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35338485 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
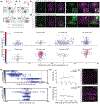
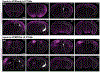
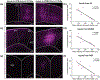
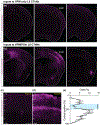
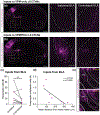
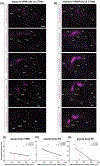
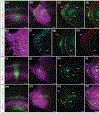
Although corticothalamic neurons (CThNs) represent the largest source of synaptic input to thalamic neurons, their role in regulating thalamocortical interactions remains incompletely understood. CThNs in sensory cortex have historically been divided into two types, those with cell bodies in Layer 6 (L6) that project back to primary sensory thalamic nuclei and those with cell bodies in Layer 5 (L5) that project to higher-order thalamic nuclei and subcortical structures. Recently, diversity among L6 CThNs has increasingly been appreciated. In the rodent somatosensory cortex, two major classes of L6 CThNs have been identified: one projecting to the ventral posterior medial nucleus (VPM-only L6 CThNs) and one projecting to both VPM and the posterior medial nucleus (VPM/POm L6 CThNs). Using rabies-based tracing methods in mice, we asked whether these L6 CThN populations integrate similar synaptic inputs. We found that both types of L6 CThNs received local input from somatosensory cortex and thalamic input from VPM and POm. However, VPM/POm L6 CThNs received significantly more input from a number of additional cortical areas, higher order thalamic nuclei, and subcortical structures. We also found that the two types of L6 CThNs target different functional regions within the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN). Together, our results indicate that these two types of L6 CThNs represent distinct information streams in the somatosensory cortex and suggest that VPM-only L6 CThNs regulate, via their more restricted circuits, sensory responses related to a cortical column while VPM/POm L6 CThNs, which are integrated into more widespread POm-related circuits, relay contextual information.
Keywords: corticothalamic neurons; layer 6; rabies virus; somatosensory cortex; thalamic reticular nucleus; trans-synaptic tracing.
© 2021 The Authors. The Journal of Comparative Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

