Paraaortic sentinel lymph node detection in intermediate and high-risk endometrial cancer by transvaginal ultrasound-guided myometrial injection of radiotracer (TUMIR)
- PMID: 33908710
- PMCID: PMC8192237
- DOI: 10.3802/jgo.2021.32.e52
Paraaortic sentinel lymph node detection in intermediate and high-risk endometrial cancer by transvaginal ultrasound-guided myometrial injection of radiotracer (TUMIR)
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to evaluate the accuracy of sentinel lymph node (SLN) mapping with transvaginal ultrasound-guided myometrial injection of radiotracer (TUMIR) to detect lymph node (LN) metastases, in patients with intermediate and high-risk endometrial cancer (EC), focusing on its performance to detect paraaortic involvement.
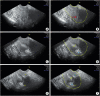
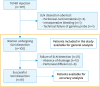
Methods: Prospective study including women with preoperative intermediate or high-risk EC, according to ESMO-ESGO-ESTRO consensus, who underwent SLN mapping using the TUMIR approach. SLNs were preoperatively localized by planar and single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography images, and intraoperatively by gamma-probe. Immediately after SLN excision, all women underwent systematic pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenectomy by laparoscopy.
Results: The study included 102 patients. The intraoperative SLN detection rate was 79.4% (81/102). Pelvic and paraaortic drainage was observed in 92.6% (75/81) and 45.7% (37/81) women, respectively, being exclusively paraaortic in 7.4% (6/81). After systematic lymphadenectomy, LN metastases were identified in 19.6% (20/102) patients, with 45.0% (9/20) showing paraaortic involvement, which was exclusive in 15.0% (3/20). The overall sensitivity and negative predictive value (NPV) of SLNs by the TUMIR approach to detect lymphatic involvement were 87.5% and 97.0%, respectively; and 83.3% and 96.9%, for paraaortic metastases. After applying the MSKCC SLN mapping algorithm, the sensitivity and NPV were 93.8% and 98.5%, respectively.
Conclusion: The TUMIR method provides valuable information of endometrial drainage in patients at higher risk of paraaortic LN involvement. The TUMIR approach showed a detection rate of paraaortic SLNs greater than 45% and a high sensitivity and NPV for paraaortic metastases in women with intermediate and high-risk EC.
Keywords: Endometrial Neoplasms; Genital Neoplasms, Female; Lymph Node Excision; Sensitivity and Specificity; Sentinel Lymph Node; Surgery.
Copyright © 2021. Asian Society of Gynecologic Oncology, Korean Society of Gynecologic Oncology, and Japan Society of Gynecologic Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
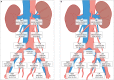
Comment in
-
How to perform sentinel node detection in high-risk endometrial cancer: one step forward.J Gynecol Oncol. 2021 Jul;32(4):e71. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2021.32.e71. J Gynecol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34085801 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Touhami O, Grégoire J, Renaud MC, Sebastianelli A, Plante M. Performance of sentinel lymph node (SLN) mapping in high-risk endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2017;147:549–553. - PubMed
-
- Altay A, Toptas T, Dogan S, Simsek T, Pestereli E. Analysis of metastatic regional lymph node locations and predictors of para-aortic lymph node involvement in endometrial cancer patients at risk for lymphatic dissemination. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015;25:657–664. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

