Evaluation of the mediastinal-thoracic volume ratio on postmortem computed tomography
- PMID: 33909145
- PMCID: PMC8354949
- DOI: 10.1007/s00414-021-02593-0
Evaluation of the mediastinal-thoracic volume ratio on postmortem computed tomography
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to measure the mediastinal-thoracic volume ratio (CTR_VOL) on PMCT as a more accurate version of traditional CTR, in order to assess the terminal positional relationship between the heart and lungs in the different causes of death with regard to age, gender, BMI, cardiomegaly, and lung expansion.
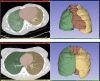
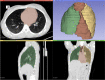
Materials: Two hundred fifty consecutive postmortem cases with pre-autopsy PMCT and full forensic autopsy were retrospectively evaluated. The lungs and the mediastinum were manually segmented on the PMCT data and the correspondent volumes were estimated in situ. CTR_VOL was calculated as the ratio of the mediastinal to the thoracic volume. The volume measurements were repeated by the same rater for the evaluation of the intrarater reliability. Age, gender, body weight and height, heart weight at autopsy, and cause of death were retrieved from the autopsy reports. Presence of lung expansion was radiologically evaluated in situ.
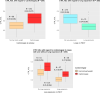
Results: CTR_VOL was positively associated with age and BMI but not with gender and was higher for cardiomegaly compared to normal hearts, lower for asphyxiation-related deaths compared to cardiac deaths and intoxications, and lower for cases with lung expansion. The intrarater reliability was excellent for the calculated volumes of both lungs and mediastinum.
Conclusion: The results of the present study support CTR_VOL as a tool to assess the relationship between the heart and lungs in situ, which differs significantly between the studied cause of death categories.
Keywords: Cardiothoracic ratio; Cause of death; Postmortem computed tomography; Segmentation; Three-dimensional (3D); Virtopsy.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no conflicts of interest and no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cardiothoracic ratio in postmortem computed tomography: reliability and threshold for the diagnosis of cardiomegaly.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2014 Mar;10(1):44-9. doi: 10.1007/s12024-013-9504-9. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24174274
-
Cardiothoracic ratio in postmortem chest radiography with regard to the cause of death.Leg Med (Tokyo). 2010 Mar;12(2):73-8. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2009.11.007. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2010. PMID: 20116320
-
Postmortem virtual volumetry of the heart and lung in situ using CT data for investigating terminal cardiopulmonary pathophysiology in forensic autopsy.Leg Med (Tokyo). 2014 Jul;16(4):187-92. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2014. PMID: 24703760
-
Postmortem diagnosis of arterial atherosclerosis in autopsy, postmortem computed tomography and histopathological examinations in medico-legal aspect.Arch Med Sadowej Kryminol. 2024;74(1):50-63. doi: 10.4467/16891716AMSIK.24.004.19649. Arch Med Sadowej Kryminol. 2024. PMID: 39450595 Review. English, Polish.
-
Post-mortem CT imaging of the lungs: pathological versus non-pathological findings.Radiol Med. 2017 Dec;122(12):902-908. doi: 10.1007/s11547-017-0802-2. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Radiol Med. 2017. PMID: 28836139 Review.
Cited by
-
The current state of forensic imaging - post mortem imaging.Int J Legal Med. 2025 May;139(3):1141-1159. doi: 10.1007/s00414-025-03461-x. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Int J Legal Med. 2025. PMID: 40126650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thoracic mediastinal-occupying ratio predicts recovery and prognosis after lung transplantation.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2022 Aug 3;35(3):ivac106. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivac106. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2022. PMID: 35445700 Free PMC article.
-
The Current Status of Virtual Autopsy Using Combined Imaging Modalities: A Scoping Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 25;14(3):782. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030782. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weissleder R, Wittenberg J, Harisinghani MG. Primer of diagnostic imaging. 5. St.Louis: Elsevier/Mosby; 2011.
-
- Jotterand M, Doenz F, Grabherr S, et al (2016) The cardiothoracic ratio on post-mortem computer tomography. Int J Legal Med 1309–1313 - PubMed
-
- Jotterand M, Faouzi M, Dedouit F, Michaud K (2019) New formula for cardiothoracic ratio for the diagnosis of cardiomegaly on post-mortem CT. Int J Leg Med. 10.1007/s00414-019-02113-1 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

