New promising drugs for the treatment of systemic sclerosis: pathogenic considerations, enhanced classifications, and personalized medicine
- PMID: 33909517
- PMCID: PMC8292968
- DOI: 10.1080/13543784.2021.1923693
New promising drugs for the treatment of systemic sclerosis: pathogenic considerations, enhanced classifications, and personalized medicine
Abstract
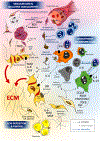
Introduction: Systemic sclerosis (SSc), also known as scleroderma, is a complex orphan disease characterized by early inflammatory features, vascular hyper-reactivity, and fibrosis of the skin and internal organs. Although substantial progress has been made in the understanding of the pathogenesis of SSc, there is still no disease-modifying drug that could significantly impact the natural history of the disease.Areas covered: This review discusses the rationale, preclinical evidence, first clinical eevidence,and pending issues concerning new promising therapeutic options that are under investigation in SSc. The search strategy was based on PubMed database and clinical trial.gov, highlighting recent key pathogenic aspects and phase I or II trials of investigational drugs in SSc.Expert opinion: The identification of new molecular entities that potentially impact inflammation and fibrosis may constitute promising options for a disease modifying-agent in SSc. The early combinations of antifibrotic drugs (such as pirfenidone) with immunomodulatory agents (such as mycophenolate mofetil) may also participate to achieve such a goal. A more refined stratification of patients, based on clinical features, molecular signatures, and identification of subpopulations with distinct clinical trajectories, may also improve management strategies in the future.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; fibrosis; investigational drugs; macrophages; myofibroblasts; scleroderma; systemic sclerosis; vasculopathy.
Figures

References
-
- Allanore Y, Simms R, Distler O, Trojanowska M, Pope J, Denton CP, et al. Systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015;1:15002. - PubMed
-
- Hughes M, Allanore Y, Chung L, Pauling JD, Denton CP, Matucci-Cerinic M. Raynaud phenomenon and digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2020;16:208–221. - PubMed
-
- Denton CP, Khanna D. Systemic sclerosis. The Lancet 2017;390:1685–1699. - PubMed
-
-
Distler O, Highland KB, Gahlemann M, Azuma A, Fischer A, Mayes MD, et al. Nintedanib for Systemic Sclerosis–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2019;380:2518–2528.
** This phase III trial demonstrates the efficacy of FDA-approved nintedanib to limit FVC decline in SSc-ILD
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
