Emergence of immunosuppressive LOX-1+ PMN-MDSC in septic shock and severe COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 33909917
- PMCID: PMC8242532
- DOI: 10.1002/JLB.4COVBCR0321-129R
Emergence of immunosuppressive LOX-1+ PMN-MDSC in septic shock and severe COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
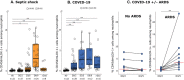
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) are a heterogeneous population of immature myeloid cells with immunosuppressive properties. In cancer patients, the expression of lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor 1 (LOX-1) on granulocytic MDSC identifies a subset of MDSC that retains the most potent immunosuppressive properties. The main objective of the present work was to explore the presence of LOX-1+ MDSC in bacterial and viral sepsis. To this end, whole blood LOX-1+ cells were phenotypically, morphologically, and functionally characterized. They were monitored in 39 coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19, viral sepsis) and 48 septic shock (bacterial sepsis) patients longitudinally sampled five times over a 3 wk period in intensive care units (ICUs). The phenotype, morphology, and immunosuppressive functions of LOX-1+ cells demonstrated that they were polymorphonuclear MDSC. In patients, we observed the significant emergence of LOX-1+ MDSC in both groups. The peak of LOX-1+ MDSC was 1 wk delayed with respect to ICU admission. In COVID-19, their elevation was more pronounced in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. The persistence of these cells may contribute to long lasting immunosuppression leaving the patient unable to efficiently resolve infections.
Keywords: HLA-DR; flow cytometry; immunosuppression; sepsis.
©2021 Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Veglia F, Sanseviero E, Gabrilovich DI. Myeloid‐derived suppressor cells in the era of increasing myeloid cell diversity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;1:1‐14. https://doi.org.10.1038/s41577-020-00490-y. Online ahead of print. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

