Inhibition of mitochondrial translation suppresses glioblastoma stem cell growth
- PMID: 33910005
- PMCID: PMC8097689
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109024
Inhibition of mitochondrial translation suppresses glioblastoma stem cell growth
Abstract
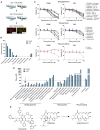
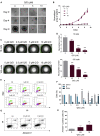
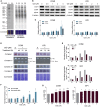
Glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) resist current glioblastoma (GBM) therapies. GSCs rely highly on oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), whose function requires mitochondrial translation. Here we explore the therapeutic potential of targeting mitochondrial translation and report the results of high-content screening with putative blockers of mitochondrial ribosomes. We identify the bacterial antibiotic quinupristin/dalfopristin (Q/D) as an effective suppressor of GSC growth. Q/D also decreases the clonogenicity of GSCs in vitro, consequently dysregulating the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis. Cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) reveals that Q/D binds to the large mitoribosomal subunit, inhibiting mitochondrial protein synthesis and functionally dysregulating OXPHOS complexes. These data suggest that targeting mitochondrial translation could be explored to therapeutically suppress GSC growth in GBM and that Q/D could potentially be repurposed for cancer treatment.
Keywords: OXPHOS; cryo-EM; dalfopristin; drug repurposing; glioblastoma; glioblastoma stem cells; high-content screening; mitochondrial translation; mitoribosome; quinupristin.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.S., I.M., A.M., and A.Q. have applied for protection of intellectual property related to the results in the manuscript and to Q/D analogs in cancer therapy (Italian patent number 102020000012601).
Figures




References
-
- Angeletti F., Fossati G., Pattarozzi A., Würth R., Solari A., Daga A., Masiello I., Barbieri F., Florio T., Comincini S. Inhibition of the Autophagy Pathway Synergistically Potentiates the Cytotoxic Activity of Givinostat (ITF2357) on Human Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016;9:107. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashton T.M., McKenna W.G., Kunz-Schughart L.A., Higgins G.S. Oxidative Phosphorylation as an Emerging Target in Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018;24:2482–2490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

