Reactive astrocytes facilitate vascular repair and remodeling after stroke
- PMID: 33910014
- PMCID: PMC8142687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109048
Reactive astrocytes facilitate vascular repair and remodeling after stroke
Abstract
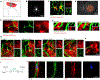
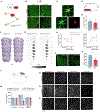
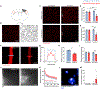
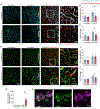
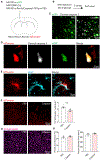
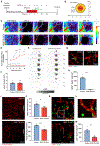
Brain injury causes astrocytes to assume a reactive state that is essential for early tissue protection, but how reactive astrocytes affect later reparative processes is incompletely understood. In this study, we show that reactive astrocytes are crucial for vascular repair and remodeling after ischemic stroke in mice. Analysis of astrocytic gene expression data reveals substantial activation of transcriptional programs related to vascular remodeling after stroke. In vivo two-photon imaging provides evidence of astrocytes contacting newly formed vessels in cortex surrounding photothrombotic infarcts. Chemogenetic ablation of a subset of reactive astrocytes after stroke dramatically impairs vascular and extracellular matrix remodeling. This disruption of vascular repair is accompanied by prolonged blood flow deficits, exacerbated vascular permeability, ongoing cell death, and worsened motor recovery. In contrast, vascular structure in the non-ischemic brain is unaffected by focal astrocyte ablation. These findings position reactive astrocytes as critical cellular mediators of functionally important vascular remodeling during neural repair.
Keywords: angiogenesis; astrocytes; blood-brain barrier; neural repair; recovery; revascularization; stroke; vascular remodeling.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Allegra Mascaro AL, Conti E, Lai S, Di Giovanna AP, Spalletti C, Alia C, Panarese A, Scaglione A, Sacconi L, Micera S, et al. (2019). Combined rehabilitation promotes the recovery of structural and functional features of healthy neuronal networks after stroke. Cell Rep. 28, 3474–3485.e6. - PubMed
-
- Androvic P, Kirdajova D, Tureckova J, Zucha D, Rohlova E, Abaffy P, Kriska J, Valny M, Anderova M, Kubista M, and Valihrach L (2020). Decoding the transcriptional response to ischemic stroke in young and aged mouse brain. Cell Rep. 31, 107777. - PubMed
-
- Baskin YK, Dietrich WD, and Green EJ (2003). Two effective behavioral tasks for evaluating sensorimotor dysfunction following traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neurosci. Methods 129, 87–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

