SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnant Women: Neuroimmune-Endocrine Changes at the Maternal-Fetal Interface
- PMID: 33910207
- PMCID: PMC8247841
- DOI: 10.1159/000515556
SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnant Women: Neuroimmune-Endocrine Changes at the Maternal-Fetal Interface
Abstract
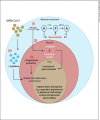
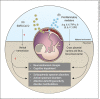
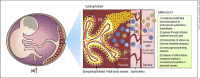
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has devastating effects on the population worldwide. Given this scenario, the extent of the impact of the disease on more vulnerable individuals, such as pregnant women, is of great concern. Although pregnancy may be a risk factor in respiratory virus infections, there are no considerable differences regarding COVID-19 severity observed between pregnant and nonpregnant women. In these circumstances, an emergent concern is the possibility of neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric harm for the offspring of infected mothers. Currently, there is no stronger evidence indicating vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2; however, the exacerbated inflammatory response observed in the disease could lead to several impairments in the offspring's brain. Furthermore, in the face of historical knowledge on possible long-term consequences for the progeny's brain after infection by viruses, we must consider that this might be another deleterious facet of COVID-19. In light of neuroimmune interactions at the maternal-fetal interface, we review here the possible harmful outcomes to the offspring brains of mothers infected by SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Maternal-fetal interface; Neurodevelopment; Neuroimmune interactions; Pregnancy; Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2.
© 2021 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Drosten C, Günther S, Preiser W, Van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S, et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348((20)):1967. - PubMed
-
- Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, Chan P, Cameron P, Joynt GM, et al. A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med. 2003;348((20)):1986. - PubMed
-
- Zaki AM, Van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367((19)):1814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

