[CD45RO⁺ Memory T Lymphocytes As A Candidate Marker for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer]
- PMID: 33910273
- PMCID: PMC8105606
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2021.103.05
[CD45RO⁺ Memory T Lymphocytes As A Candidate Marker for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer]
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is the most common malignancy world-wide. There are a variety of immune infiltrating cells in tumor microenvironment, which is an important component of tumor immunity and has clinical significance for the prognosis of patients. CD45RO is a surface marker of memory T cells. The expression of CD45RO⁺ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) is associated with the prognosis of many tumors. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the density of CD45RO⁺ TILs in tumor and stromal area and the clinical characteristics of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and its impact on the prognosis of patients. We aimed to explore the clinical value of CD45RO⁺ TILs and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) as prognostic markers.
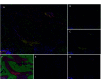
Methods: Multiple fluorescent immunohistochemical staining was used to stain the tissue microarray chips of 167 patients with NSCLC, marking CD45RO, cytokeratin (CK) and PD-L1. Using artificial intelligence image recognition technology and tumor cell-specific CK staining, divide the tumor and stromal area in the tissue, evaluate the density of CD45RO⁺ TILs in the tumor and stromal area, and the expression level of PD-L1 in tumor cells. The non-parametric test was used to analyze the relationship between CD45RO⁺ TILs and the clinical characteristics of patients, and the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox risk ratio model were used to analyze the relationship between CD45RO⁺ TILs independently or in combination with PD-L1 and tumor prognosis.
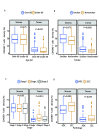
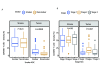
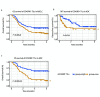
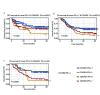
Results: The density of CD45RO⁺ TILs was significantly associated with patient age, smoking, tumor stage, and pathological type. Single-factor survival analysis showed that NSCLC (P=0.007) stromal region and lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) (P<0.001) with CD45RO⁺ TILs high density had better OS. Multivariate survival analysis showed that the high density of CD45RO⁺ TILs in the stromal region of NSCLC (HR=0.559, 95%CI: 0.377-0.829, P=0.004) and lung adenocarcinoma (HR=0.352, 95%CI: 0.193-0.641, P=0.001) were independent prognostic factors for overall survival time (OS). Combined with PD-L1 score of tumor cells in tumor tissues and infiltration score of CD45RO⁺ TILs in all tumor tissues, the patients were divided into 4 groups: patients with PD-L1⁺/CD45RO⁺ had the longest disease-free survival (DFS) time, and patients with PD-L1⁺/CD45RO- had the shortest DFS time. Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that PD-L1⁺/CD45RO- was an independent prognostic factor for DFS and had a higher risk of poor prognosis compared to the other three groups (HR=2.221, 95%CI: 1.258-3.919, P=0.006).
Conclusions: In tumor tissues, the density of CD45RO⁺ TILs, as well as the combination of CD45RO⁺ TILs and PD-L1 in tumor areas, significantly correlated with clinicopathological features and prognosis of NSCLC, which can be used as a new prognosis marker.
【中文题目:CD45RO⁺记忆T细胞作为非小细胞肺癌患者 预后标志物的研究】 【中文摘要:背景与目的 肺癌是世界范围内最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。肿瘤微环境中多种多样的免疫浸润细胞,是肿瘤免疫的重要组成,对患者预后具有临床意义。CD45RO⁺肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, TILs),即记忆T细胞,其表达与多种肿瘤预后相关。本研究旨在探讨非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)中评估肿瘤和基质区CD45RO⁺ TILs密度与患者临床特征和预后的关系,及其联合程序性死亡受体配体1(programmed cell death-ligand 1, PD-L1)作为预后标志物的临床价值。方法 对167例NSCLC患者的组织微阵列进行多重荧光免疫组织化学染色,标记CD45RO、细胞角蛋白(cytokeratin, CK)和PD-L1。利用人工智能图像识别技术和肿瘤细胞特异性CK染色,划分组织中的肿瘤区和基质区,评估肿瘤区和基质区CD45RO⁺ TILs的密度以及肿瘤细胞的PD-L1表达水平。采用非参检验分析CD45RO⁺ TILs与患者临床特征的关系,使用Kaplan-Meier方法和Cox风险比例模型分析CD45RO⁺ TILs独立或与PD-L1联合与肿瘤预后的关系。结果 CD45RO⁺ TILs的密度与患者年龄、吸烟、肿瘤分期和病理类型显著相关。在NSCLC和肺腺癌(lung adenocarcinoma, LUAD)患者中,基质区高密度CD45RO⁺ TILs具有更长的总生存期(overall survival, OS)(NSCLC: P=0.007; LUAD: P<0.001),并且是OS的独立预后因素(NSCLC: HR=0.559, 95%CI: 0.377-0.829, P=0.004; LUAD: HR=0.352, 95%CI: 0.193-0.641, P=0.001)。联合肿瘤细胞的PD-L1评分以及所有区域CD45RO⁺ TILs的浸润评分将患者分为四组:其中PD-L1⁺/CD45RO⁺患者无病生存期(disease-free survival, DFS)最长,PD-L1⁺/CD45RO-的患者DFS时间最短,并可作为DFS预后的独立因素(HR=2.221, 95%CI: 1.258-3.919, P=0.006)。结论 肿瘤组织中CD45RO⁺ TILs密度以及CD45RO⁺ TILs联合肿瘤区PD-L1,与NSCLC的临床病理特征及预后显著相关,可作为新的生存预后标志物。】 【中文关键词:肺肿瘤;CD45RO;程序性死亡受体-配体1;预后】.
Keywords: CD45RO; Lung neoplasms; Prognosis; Programmed cell death ligand 1.
Conflict of interest statement
【
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of PD-L1 expression in combination with CD8+ TILs density in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2018 Jan;7(1):32-45. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1243. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 29168339 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression combined with CD8 tumor infiltrating lymphocytes density in non-small cell lung cancer patients.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2018 Dec;30(4):125-131. doi: 10.1016/j.jnci.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Oct 15. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2018. PMID: 30337185
-
Clinicopathological correlation of PD-L1 and TET1 expression with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in non-small cell lung cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Nov;216(11):153188. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153188. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32919305
-
Association between CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2023 Jun;23(6):643-659. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2023.2208351. Epub 2023 May 4. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2023. PMID: 37114477
-
Prognostic Significance of CD4+ Tumour Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Receiving PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors Therapy.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2025 Mar;35(3):341-350. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2025.03.341. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2025. PMID: 40055170
Cited by
-
Prognostic implications of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 20;15:1476365. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1476365. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39372398 Free PMC article.
-
A Thorough Review of the Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 4;17(5):882. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050882. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075729 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- West H, McCleod M, Hussein M, et al. Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower130): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(7):924–937. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30167-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

