[CRISPR/Cas9-mediated microRNA-21 knockout increased imatinib sensitivity in chronic myeloid leukemia cells]
- PMID: 33910311
- PMCID: PMC8081948
- DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2021.03.011
[CRISPR/Cas9-mediated microRNA-21 knockout increased imatinib sensitivity in chronic myeloid leukemia cells]
Abstract
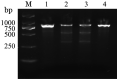
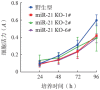
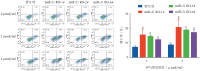
Objective: To observe the effects of miR-21 knockout on proliferation and drug resistance in K562/G01 cells, and to preliminarily explore the mechanism of imatinib sensitivity by knocking out miR-21 in K562/G01 cells. Methods: Using CRISPR/Cas9 to knock out the miR-21 gene in K562/G01 cells, and single-cell-derived clones of miR-21 knockout were obtained by genomic DNA PCR screening, Sanger sequencing, and real-time PCR. We used MTT and cell colony formation assays to assess the cell proliferation, and determined imatinib sensitivity by MTT assay and Annexin-Ⅴ-APC/7-AAD double staining flow cytometry. Using western blot, we examined the potential mechanisms affecting imatinib sensitivity by knocking out miR-21 in K562/G01 cells. Results: Three miR-21 knockout K562/G01 single-cell-derived clones were successfully constructed. The mutation efficiency mediated by CRISPR/Cas9 was 7.12%-8.11%. MiR-21 knockout inhibited the proliferation of K562/G01 cells; the clone formation rates of WT and 1#, 2#, 6# K562/G01 single-cell clones were (57.67±8.25) %, (26.94± 5.36) %, (7.17±2.11) %, (31.50±3.65) %, respectively. MiR-21 knockout increased the sensitivity of K562/G01 cells to imatinib, IC(50) of imatinib in WT, and 1#, 2#, 6# K562/G01 single-cell clones were (21.92±1.36) µmol/ml, (3.98±0.39) µmol/ml, (5.38±1.01) µmol/ml, (9.24±1.36) µmol/ml. After the knockout of miR-21, the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling molecules was inhibited, while the expression of P210(B)CR-ABL and p-P210(BCR-ABL) was downregulated; however, the expression of PTEN was not affected. Conclusion: The knockout of miR-21 can suppress cell proliferation and improve sensitivity to imatinib in K562/G01 cells, which may be achieved by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and BCR-ABL expression.
目的: 观察microRNA-21(miR-21)敲除对耐伊马替尼的人慢性髓性白血病细胞株K562/G01细胞在增殖、药物敏感性等方面的影响,初步探讨miR-21影响K562/G01细胞伊马替尼敏感性的可能机制。 方法: 运用CRISPR/Cas9技术敲除K562/G01细胞的miR-21,经PCR筛选、Sanger测序鉴定和实时定量PCR检测获得miR-21敲除的单细胞克隆。扩增培养后,采用MTT法、细胞克隆形成实验检测miR-21敲除对K562/G01细胞增殖的影响。使用伊马替尼处理细胞后,用MTT法和Annexin Ⅴ-APC/7-AAD双染流式细胞检测法观察敲除miR-21后K562/G01细胞对伊马替尼的敏感性的变化。Western blot法检测miR-21敲除前后K562/G01细胞PTEN、AKT、p-AKT、PI3K、p-PI3K、P210(BCR-ABL)、p-P210(BCR-ABL)蛋白表达量的变化。 结果: 成功构建了3个miR-21敲除的K562/G01单细胞克隆,CRISPR/Cas9介导的突变效率为7.12%~8.11%。miR-21敲除使K562/G01细胞的增殖受抑,野生型和1#、2#、6#单细胞克隆的克隆形成率依次为(57.67±8.25)%、(26.94±5.36)%、(7.17±2.11)%、(31.50±3.65)%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。miR-21敲除使K562/G01细胞对伊马替尼的敏感性增加,野生型和1#、2#、6#单细胞克隆对伊马替尼的IC(50)值分别为(21.92±1.36)µmol/ml、(3.98±0.39)µmol/ml、(5.38±1.01)µmol/ml、(9.24±1.36)µmol/ml,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。miR-21敲除后,其靶基因PTEN的蛋白表达水平未见明显变化,但PI3K、AKT信号分子的活化受到抑制,并且P210(BCR-ABL)、p-P210(BCR-ABL)蛋白表达也下调。 结论: miR-21敲除抑制K562/G01细胞增殖,提高其对伊马替尼的敏感性,这可能是通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路和BCR-ABL表达实现的。.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Chronic myeloid leukemia; Knockout; imatinib; miR-21.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Effect of phenylhexyl isothiocyanate on drug-resistance to imatinib in K562/G01 cell line].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Feb;34(2):149-52. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23611223 Chinese.
-
[Effect of A Novel Emodin Derivative on Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia K562 Cells and Imatinib-resistant K562/G01 Cells].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;24(1):1-7. doi: 10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2016.01.001. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26913384 Chinese.
-
[Establishment of an imatinib resistant cell line K562/G01 and its characterization].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Jun;25(6):337-41. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15308010 Chinese.
-
[MET/ERK and MET/JNK Pathway Activation Is Involved in BCR-ABL Inhibitor-resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(12):1461-1466. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00142. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 30504658 Review. Japanese.
-
Emerging Opportunities for Target Discovery in Rare Cancers.Cell Chem Biol. 2017 Sep 21;24(9):1075-1091. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.08.002. Cell Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28938087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Utilization of CRISPR-Mediated Tools for Studying Functional Genomics in Hematological Malignancies: An Overview on the Current Perspectives, Challenges, and Clinical Implications.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 28;12:767298. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.767298. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35154242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Anti-Leukemic Potential of Curcumin in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Sep 7;13(9):e70852. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70852. eCollection 2025 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40927046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

