SGLT2 inhibitors and lower limb complications: an updated meta-analysis
- PMID: 33910574
- PMCID: PMC8082772
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-021-01276-9
SGLT2 inhibitors and lower limb complications: an updated meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: SGLT2 inhibitors and lower limb complications: an updated meta-analysis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Jun 9;20(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01306-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 34107970 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: To exam the associations between the use of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) and the risk of lower limb complications, and to analyze the associated factors.
Methods: Pubmed, Medline, Embase, the Cochrane Center Register of Controlled Trials for Studies and Clinicaltrial.gov were searched from the inception to November 2020. Randomized controlled trials of SGLT2i conducted in population containing diabetic patients with reports of amputation, peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and diabetic foot (DF) events were included. Random-effect model, fixed-effect model and meta-regression analysis were accordingly used.
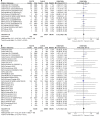
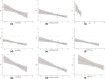
Result: The numbers of SGLT2i users versus non-SGLT2i users in the analyses of amputation, PAD and DF were 40,925/33,414, 36,446/28,685 and 31,907/25,570 respectively. Compared with non-SGLT2i users, the risks of amputation and PAD were slightly increased in patients with canagliflozin treatment (amputation: OR = 1.60, 95% CI 1.04 to 2.46; PAD: OR = 1.53, 95 % CI 1.14 to 2.05). Meta-regression analyses indicated that greater weight reduction in SGLT2i users was significantly associated with the increased risks of amputation (β = - 0.461, 95% CI - 0.726 to - 0.197), PAD (β = - 0.359, 95% CI - 0.545 to - 0.172) and DF (β = - 0.476, 95% CI - 0.836 to - 0.116). Lower baseline diastolic blood pressure (β = - 0.528, 95% CI - 0.852 to - 0.205), more systolic blood pressure reduction (β = - 0.207, 95% CI - 0.390 to - 0.023) and more diastolic blood pressure reduction (β = - 0.312, 95% CI - 0.610 to - 0.015) were significantly associated with the increased risks of amputation, PAD and DF respectively in patients with SGLT2i treatment.
Conclusions: The risks of amputation and PAD were slightly increased in patients with canagliflozin treatment. Reductions in body weight and blood pressure were associated with lower limb complications in patients with SGLT2i treatment.
Keywords: Amputation; Blood pressure lowering agent; Diabetes mellitus; Diabetic foot; Peripheral arterial disease; Sodium glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
LJ has received fees for lecture presentations and for consulting from AstraZeneca, Merck, Metabasis, MSD, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis and Takeda. All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures
Comment in
-
SGLT2 inhibitors and lower limb complications: the diuretic-induced hypovolemia hypothesis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 May 13;20(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01301-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33985506 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Comparative effectiveness of canagliflozin, SGLT2 inhibitors and non-SGLT2 inhibitors on the risk of hospitalization for heart failure and amputation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world meta-analysis of 4 observational databases (OBSERVE-4D).Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Nov;20(11):2585-2597. doi: 10.1111/dom.13424. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29938883 Free PMC article.
-
Risks of diabetic foot syndrome and amputation associated with sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Diabetes Metab. 2018 Nov;44(5):410-414. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Diabetes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29506779
-
Initiation of SGLT2 Inhibitors and the Risk of Lower Extremity Minor and Major Amputation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Health Claims Data Analysis.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Dec;62(6):981-990. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.09.031. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 34782230
-
Association between sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and lower extremity amputation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 5;15(6):e0234065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234065. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32502190 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) use and risk of amputation: an expert panel overview of the evidence.Metabolism. 2019 Jul;96:92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.04.008. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Metabolism. 2019. PMID: 30980838 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use and diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of real-world studies.BMC Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun 28;24(1):272. doi: 10.1186/s12886-024-03535-1. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38943083 Free PMC article.
-
The use of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists versus sulfonylureas and the risk of lower limb amputations: a nation-wide cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Jun 29;22(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01897-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37386427 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the cardio-renal-metabolic-foot connection in people with diabetes-related foot ulceration: a narrative review.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Dec 18;23(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02527-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39696281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative safety of different recommended doses of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 10;14:1256548. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1256548. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38027214 Free PMC article.
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in PAD: A State-of-the-Art Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Aug 6;14(15):5549. doi: 10.3390/jcm14155549. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40807170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Miyashita S, Kuno T, Takagi H, Sugiyama T, Ando T, Valentin N, Shimada YJ, Kodaira M, Numasawa Y, Kanei Y, Bangalore S. Risk of amputation associated with sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors: a meta-analysis of five randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;163:108136. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108136. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

