CCL19 and CCL28 Assist Herpes Simplex Virus 2 Glycoprotein D To Induce Protective Systemic Immunity against Genital Viral Challenge
- PMID: 33910988
- PMCID: PMC8092132
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00058-21
CCL19 and CCL28 Assist Herpes Simplex Virus 2 Glycoprotein D To Induce Protective Systemic Immunity against Genital Viral Challenge
Abstract
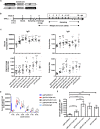
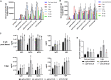
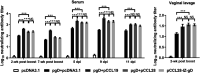
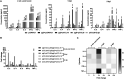
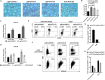
Potent systemic immunity is important for recalled mucosal immune responses, but in the defense against mucosal viral infections, it usually remains low at mucosal sites. Based on our previous findings that enhanced immune responses can be achieved by immunization with an immunogen in combination with a molecular adjuvant, here we designed chemokine-antigen (Ag) fusion constructs (CCL19- or CCL28-herpes simplex virus 2 glycoprotein D [HSV-2 gD]). After intramuscular (i.m.) immunization with different DNA vaccines in a prime and boost strategy, BALB/c mice were challenged with a lethal dose of HSV-2 through the genital tract. Ag-specific immune responses and chemokine receptor-specific lymphocytes were analyzed to determine the effects of CCL19 and CCL28 in strengthening humoral and cellular immunity. Both CCL19 and CCL28 were efficient in inducing long-lasting HSV-2 gD-specific systemic immunity. Compared to CCL19, less CCL28 was required to elicit HSV-2 gD-specific serum IgA responses, Th1- and Th2-like responses of immunoglobulin (Ig) subclasses and cytokines, and CCR3+ T cell enrichment (>8.5-fold) in spleens. These findings together demonstrate that CCL28 tends to assist an immunogen to induce more potently protective immunity than CCL19. This work provides information for the application potential of a promising vaccination strategy against mucosal infections caused by HSV-2 and other sexually transmitted viruses.IMPORTANCE An effective HSV-2 vaccine should induce antigen (Ag)-specific immune responses against viral mucosal infection. This study reveals that chemokine CCL19 or CCL28 enhanced HSV-2 glycoprotein D ectodomain (gD-306aa)-induced immune responses against vaginal virus challenge. In addition to eliciting robust humoral immune responses, the chemokine-Ag fusion construct also induced Th1- and Th2-like immune responses characterized by the secretion of multiple Ig subclasses and cytokines that were able to be recalled after HSV-2 challenge, while CCL28 appeared to be more effective than CCL19 in promoting gD-elicited immune responses as well as the migration of T cells to secondary lymph tissues. Of importance, both CCL19 and CCL28 significantly facilitated gD to induce protective mucosal immune responses in the genital tract. The above-described findings together highlight the potential of CCL19 or CCL28 in combination with gD as a vaccination strategy to control HSV-2 infection.
Keywords: CCL19; CCL28; HSV-2; glycoprotein D; mucosal immunity.
Copyright © 2021 Yan et al.
Figures
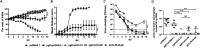
Similar articles
-
Immunization with HSV-2 gB-CCL19 Fusion Constructs Protects Mice against Lethal Vaginal Challenge.J Immunol. 2015 Jul 1;195(1):329-38. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500198. Epub 2015 May 20. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25994965
-
Nasal and skin delivery of IC31(®)-adjuvanted recombinant HSV-2 gD protein confers protection against genital herpes.Vaccine. 2012 Jun 19;30(29):4361-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.02.019. Vaccine. 2012. PMID: 22682292
-
Rectal immunization generates protective immunity in the female genital tract against herpes simplex virus type 2 infection: relative importance of myeloid differentiation factor 88.Antiviral Res. 2008 Jun;78(3):202-14. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2007.12.014. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Antiviral Res. 2008. PMID: 18276020
-
Herpes simplex virus type 2 vaccines: new ground for optimism?Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004 May;11(3):437-45. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.11.3.437-445.2004. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15138167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The challenge of developing a herpes simplex virus 2 vaccine.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012 Dec;11(12):1429-40. doi: 10.1586/erv.12.129. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012. PMID: 23252387 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CCL28 Enhances HSV-2 gB-Specific Th1-Polarized Immune Responses against Lethal Vaginal Challenge in Mice.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Aug 10;10(8):1291. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10081291. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36016177 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic adjuvants: A paradigm shift in vaccine development and immune modulation.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025 Apr 8;36(2):102536. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102536. eCollection 2025 Jun 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 40336572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunisation Using Novel DNA Vaccine Encoding Virus Membrane Fusion Complex and Chemokine Genes Shows High Protection from HSV-2.Viruses. 2022 Oct 22;14(11):2317. doi: 10.3390/v14112317. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36366414 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines and chemokines: The vital role they play in herpes simplex virus mucosal immunology.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 23;13:936235. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.936235. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36211447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucosal CCL28 Chemokine Improves Protection against Genital Herpes through Mobilization of Antiviral Effector Memory CCR10+CD44+ CD62L-CD8+ T Cells and Memory CCR10+B220+CD27+ B Cells into the Infected Vaginal Mucosa.J Immunol. 2023 Jul 1;211(1):118-129. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300093. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37222480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoshino Y, Dalai SK, Wang K, Pesnicak L, Lau TY, Knipe DM, Cohen JI, Straus SE. 2005. Comparative efficacy and immunogenicity of replication-defective, recombinant glycoprotein, and DNA vaccines for herpes simplex virus 2 infections in mice and guinea pigs. J Virol 79:410–418. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.1.410-418.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
