MicroRNA-384 inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and metastasis via binding to Smad5 and suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin axis
- PMID: 33911345
- PMCID: PMC8035371
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-021-00458-3
MicroRNA-384 inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and metastasis via binding to Smad5 and suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin axis
Abstract
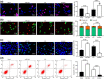
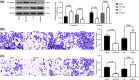
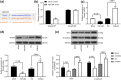
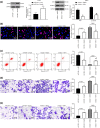
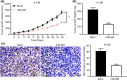
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a major otorhinolaryngological disease with limited effective therapeutic options. This work focused on the function of microRNA-384 (miR-384) on the NPC pathogenesis and the molecules involved. miR-384 expression in cancer tissues and cells was detected. Gain- and loss-of-functions of miR-384 were performed to identify its role in NPC progression. The target mRNA of miR-384 was predicted on an online system and validated through a luciferase reporter assay. The activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling was detected. Consequently, miR-384 was found to be poorly expressed in NPC tissues and cell lines and was linked to unfavorable survival rates in patients. Overexpression of miR-384 in 6-10B cells suppressed growth, migration, invasion and resistance to apoptosis of cells, but inverse trends were presented in C6661 cells where miR-384 was downregulated. miR-384 targeted Smad5 mRNA. Upregulation of Smad5 counteracted the roles of miR-384 mimic in cells. The NPC-inhibiting effects of miR-384 mimic were also blocked by Wnt/β-catenin activation. To conclude, miR-384 targets Smad5 and inactivates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which exerts a suppressing role in NPC cell behaviors as well as tumor growth in vivo. The findings may offer novel thoughts into NPC therapy.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10616-021-00458-3.
Keywords: Apoptosis; MicroRNA-384; Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; Proliferation; Smad5; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures
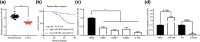
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-506 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by down-regulating LHX2.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 21;38(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1023-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. Retraction in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Sep 30;40(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02113-3. PMID: 30791932 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
miR-124 suppresses proliferation and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting Capn4.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 May 23;10:2711-2720. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S135563. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28579809 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA SMAD5-AS1 acts as a microRNA-106a-5p sponge to promote epithelial mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.FASEB J. 2019 Nov;33(11):12915-12928. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900803R. Epub 2019 Sep 26. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31557058 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-215 promoted the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through targeting RB1 and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J BUON. 2020 May-Jun;25(3):1579-1586. J BUON. 2020. PMID: 32862607
-
The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Targets miR-34a-5p and Drives Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Progression via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.Yonsei Med J. 2019 Apr;60(4):336-345. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.4.336. Yonsei Med J. 2019. PMID: 30900419 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Luteolin attenuates the chemoresistance of osteosarcoma through inhibiting the PTN/β-catenin/MDR1 signaling axis by upregulating miR-384.J Bone Oncol. 2022 Apr 13;34:100429. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2022.100429. eCollection 2022 Jun. J Bone Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35493691 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: pathogenic role and therapeutic target.Mol Cancer. 2022 Jul 14;21(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01616-7. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35836256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

