Utilization of Healthcare Resources in Osteoarthritis: A Cost of Illness Analysis Based on Real-World Data in Italy
- PMID: 33911870
- PMCID: PMC8072261
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S301005
Utilization of Healthcare Resources in Osteoarthritis: A Cost of Illness Analysis Based on Real-World Data in Italy
Abstract
Purpose: Understand the demographics and clinical features of patients with osteoarthritis (OA), quantify healthcare resource utilization by OA patients, and estimate the annual direct medical costs per OA patient from a National Health Service (NHS) perspective in Italy.
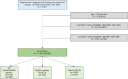
Patients and methods: Retrospective observational cohort analysis using data from electronic medical records captured by the Italian IQVIA Longitudinal Patient Database (LPD). Only direct medical costs reimbursed by the NHS were considered. Patients were included if they received at least one diagnosis of OA during the period from January 1 to December 31, 2018. Each patient was observed for 3 years: a 24-month baseline period preceding the index date, and a 12-month follow-up period starting at the index date.
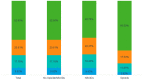
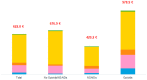
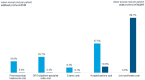
Results: A total of 71,467 patients met inclusion criteria: 43.98% had not been prescribed NSAIDs/opioids, 40.76% had been prescribed NSAIDs, and 15.26% an opioid. Mean age was 71.36 years, and 68.2% of the patients were women. At least one comorbidity was present in 91.34% of the patients; 38.05% were newly diagnosed with OA. During 1-year of follow-up, 173,884 prescriptions with an associated diagnosis of OA were found: 47.36% had been prescribed an NSAID, 9.11% diclofenac, 8.30% codeine+paracetamol, and 7.32% ketoprofen. Nearly 15% of the patients had at least 1 request for a specialist visit and 23.82% had at least 1 request for exams. Orthopedic visits accounted for 60% of all specialist visits. Yearly mean costs per patient were €622, for approximately €2.5 billion per year in direct costs, considering 3.9 million patients with OA in Italy. Protheses were a major driver in annual costs: €143.45 in patients without a prosthesis and €10,090.91 in those with a joint prosthesis.
Conclusion: This real-world analysis of direct costs of care of patients with OA in Italy confirms the substantial economic burden. Direct costs dramatically increased when joint replacement was needed.
Keywords: Italy; costs; osteoarthritis; real-world.
© 2021 Colombo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Franca Heiman and Ilaria Peduto are employees of IQVIA which received financial support to develop this manuscript. Giorgio Lorenzo Colombo has received speaker fees, research and educational grants from Abbott, Amgen, EISAI, Jazzpharma, LEO Pharma, Novo Nordisk, Merck Sharp and Dompé, Menarini, Otsuka and Pfizer. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Future projections of opioid use and cost in patients with chronic osteoarthritis pain in Spain.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021 Apr 29;13:1759720X211010599. doi: 10.1177/1759720X211010599. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021. PMID: 33995603 Free PMC article.
-
Economic Impact of Schizophrenia from a Hospital and Social Security System Perspective in Italy.Clin Drug Investig. 2021 Feb;41(2):183-191. doi: 10.1007/s40261-020-00991-7. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Clin Drug Investig. 2021. PMID: 33559103
-
Disease Burden and Costs in Moderate-to-Severe Chronic Osteoarthritis Pain Refractory to Standard of Care: Ancillary Analysis of the OPIOIDS Real-World Study.Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Mar;8(1):303-326. doi: 10.1007/s40744-020-00271-y. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Rheumatol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33411324 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Evidence of the Clinical and Economic Impact of Long-Acting Injectable Versus Oral Antipsychotics Among Patients with Schizophrenia in the United States: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.CNS Drugs. 2021 May;35(5):469-481. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00815-y. Epub 2021 Apr 28. CNS Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33909272 Free PMC article.
-
[Cost-effectiveness analysis of schizophrenic patient care settings: impact of an atypical antipsychotic under long-acting injection formulation].Encephale. 2005 Mar-Apr;31(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(05)82390-5. Encephale. 2005. PMID: 15959450 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Adherence to, and Persistence of, Antidepressant Therapy in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: Results from a Population-based Study in Italy.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(3):727-739. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220411092813. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 35410606 Free PMC article.
-
An Observational Retrospective Matched Cohort Study of Healthcare Resource Utilisation and Costs in UK Patients with Moderate to Severe Osteoarthritis Pain.Rheumatol Ther. 2022 Jun;9(3):851-874. doi: 10.1007/s40744-022-00431-2. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Rheumatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35312946 Free PMC article.
-
Drug costs in context: assessing drug costs in cost-of-illness analyses.Drugs Context. 2022 Jul 21;11:2022-5-4. doi: 10.7573/dic.2022-5-4. eCollection 2022. Drugs Context. 2022. PMID: 35949272 Free PMC article.
-
Management of osteoarthritis: From drug molecules to nano/micromedicines.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022 May;14(3):e1780. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1780. Epub 2022 Mar 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35253405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Economic and Humanistic Burden of Osteoarthritis: An Updated Systematic Review of Large Sample Studies.Pharmacoeconomics. 2023 Nov;41(11):1453-1467. doi: 10.1007/s40273-023-01296-1. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Pharmacoeconomics. 2023. PMID: 37462839
References
-
- van Saase JL, van Romunde LK, Cats A, Vandenbroucke JP, Valkenburg HA. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: zoetermeer survey. Comparison of radiological osteoarthritis in a Dutch population with that in 10 other populations. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989;48(4):271–280. doi:10.1136/ard.48.4.271 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

