Undetected Jawbone Marrow Defects as Inflammatory and Degenerative Signaling Pathways: Chemokine RANTES/CCL5 as a Possible Link Between the Jawbone and Systemic Interactions?
- PMID: 33911892
- PMCID: PMC8071694
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S307635
Undetected Jawbone Marrow Defects as Inflammatory and Degenerative Signaling Pathways: Chemokine RANTES/CCL5 as a Possible Link Between the Jawbone and Systemic Interactions?
Abstract
Background: Cytokines, especially chemokines, are of increasing interest in immunology. This study characterizes the little-known phenomenon of "bone marrow defects of the jawbone" (BMDJ) with known overexpression of the chemokine RANTES/CCL5 (R/C).
Purpose: Our investigation clarifies why BMDJ and the intensity of local R/C overexpression are challenging to detect, as examined in patients with seven different systemic immunological diseases. Specifically, we investigate whether R/C overexpression is specific to certain disease groups or if it represents a type of signal disruption found in all systemic immunological diseases.
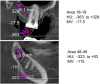
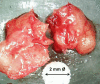
Patients and methods: In a total of 301 patients, BMDJ was surgically repaired during clinical practice to reduce "silent inflammation" associated with the presence of jaw-related pathologies. In each case of BMDJ, bone density was measured preoperatively (in Hounsfield units [HU]), while R/C expression was measured postoperatively. Each of the 301 patients suffered from allergies, atypical facial and trigeminal pain, or were diagnosed with neurodegenerative diseases, tumors, rheumatism, chronic fatigue syndrome, or parasympathetic disorders.
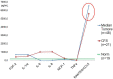
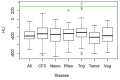
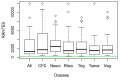
Results: In all BMDJ cases, strongly negative HU values indicated decreased bone density or osteolysis. Consistently, all cases of BMDJ showed elevated R/C expression. These findings were consistently observed in every disease group.
Discussion: BMDJ was confirmed in all patients, as verified by the HU measurements and laboratory results related to R/C expression. The hypothesis that a specific subset of the seven disease groups could be distinguished either based on the increased presence of BMDJ and by the overexpression of R/C could not be confirmed. A brief literature review confirms the importance of R/C in the etiology of each of the seven disease groups.
Conclusion: In this research, the crucial role played by BMDJ and the chemokine R/C in inflammatory and immune diseases is discussed for seven groups of patients. Each specific immune disease can be influenced or propelled by BMDJ-derived R/C inflammatory signaling pathways.
Keywords: RANTES/CCL5 inflammatory signaling pathways; bone marrow defects; jawbone; silent inflammation; systemic immune diseases.
© 2021 Lechner et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

