Effect of saline irrigation on plant water traits, photosynthesis and ionic balance in durum wheat genotypes
- PMID: 33911962
- PMCID: PMC8071897
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.01.052
Effect of saline irrigation on plant water traits, photosynthesis and ionic balance in durum wheat genotypes
Abstract
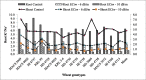
In the era of climate change, decreased precipitation and increased evapo-transpiration hampers the yield of several cereal crops along with the soil salinity and poor ground water resource. Wheat being the moderately tolerant crop face many challenges in the arid and semi-arid regions under irrigated agriculture. In view of this, the study was planned to explore the potential of durum wheat genotypes under salinity on the basis of physiological traits. Experiment was designed as RBD in three replications to evaluate 15 wheat genotypes with moderate saline irrigation (ECiw - 6 dS m-1) and extreme saline irrigation (ECiw - 10 dS m-1) along with one set of control (Best available water). Different physiological traits such as water potential (ψp), osmotic potential (ψs), relative water content (RWC), Na+ and K+ content were recorded in roots as well as shoots at the reproductive stage whereas photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll content were measured in the flag leaves. A significant variability (p < 0.001) was noted among the genotypes under different stress environments and it was observed that durum genotype HI 8728 and HI 8737 showed less reduction in plant water traits (RWC, ψp and ψs) than the salinity tolerant checks of bread wheat KRL 99 and KRL 3-4. HD 4728 and HI 8708 maintained higher photosynthetic rate as well as higher chlorophyll content under the extreme salinity level of ECiw - 10 dSm-1. No significant differences were found in root Na+ in genotypes KRL 99 (3.17g), KRL 3-4 (3.34g) and HI 8737 (3.41g) while in shoots, lowest accumulation was seen in KRL 99, MACS 3949 and KRL 3-4 at ECiw - 10 dSm-1. The mean range of K+ content was 7.60-9.74% in roots and 4.21-6.61% in shoots under control environment which decreased to 50.77% in roots and 46.05% in shoots under extreme salinity condition of ECiw - 10 dSm-1. At ECiw - 10 dSm-1, KRL 99 maintained highest K+/Na+ in both root and shoot followed by KRL 3-4, HI 8737, MACS 3949, HD 4728 in roots and MACS 3949, KRL 3-4, MACS 4020, HD 4758, MACS 3972 and HI 8713 in shoots. The differential response of durum wheat genotypes under salinity particularly for physiological traits, confer their adaptability towards stress environments and exhibit their potential as genetic sources in breeding programs for improving salt stress tolerance.
Keywords: DW, Dry weight; ECiw, Electrical conductivity of irrigation water; FW, Fresh weight; Ionic relations; MPa, Mega Pascal; Plant water relations; Pn, photosynthetic rate; RWC, Relative water content; Salinity; Wheat; ψp, Water potential; ψs, Osmotic potential.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Ashraf M. Some important physiological selection criteria for salt tolerance in plants. Flora - Morphology Distribution. Funct. Ecol. Plants. 2004;199:361–376. doi: 10.1078/0367-2530-00165. - DOI
-
- Barragan V., Leidi E., Andres Z., Rubio L., De Luca A., Fernandez J., Cubero B., Pardo J.M. Ion exchangers NHX1 and NHX2 mediate active potassium uptake into vacuoles to regulate cell turgor and stomatal function in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2012;24:1127–1142. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.095273. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

