A General Purpose Robotic Hand Exoskeleton With Series Elastic Actuation
- PMID: 33912323
- PMCID: PMC8078844
- DOI: 10.1115/1.4044543
A General Purpose Robotic Hand Exoskeleton With Series Elastic Actuation
Abstract
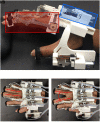
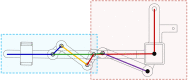
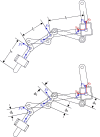
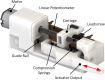
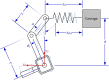
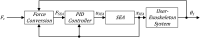
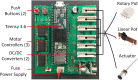
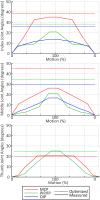
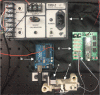
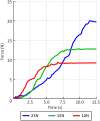
This paper describes the design and control of a novel hand exoskeleton. A subcategory of upper extremity exoskeletons, hand exoskeletons have promising applications in healthcare services, industrial workplaces, virtual reality, and military. Although much progress has been made in this field, most of the existing systems are position controlled and face several design challenges, including achieving minimal size and weight, difficulty enforcing natural grasping motions, exerting sufficient grip strength, ensuring the safety of the users hand, and maintaining overall user friendliness. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel, slim, lightweight linkage mechanism design for a hand exoskeleton with a force control paradigm enabled via a compact series elastic actuator. A detailed design overview of the proposed mechanism is provided, along with kinematic and static analyses. To validate the overall proposed hand exoskeleton system, a fully integrated prototype is developed and tested in a series of experimental trials.
Keywords: actuators and transmissions; compliant mechanisms; grasping and fixturing; multi-body dynamics and exoskelotons; wearable robots.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A SERIES ELASTIC ACTUATOR DESIGN AND CONTROL IN A LINKAGE BASED HAND EXOSKELETON.Proc ASME Dyn Syst Control Conf. 2019 Oct;2019(3):10.1115/DSCC2019-8996. doi: 10.1115/DSCC2019-8996. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Proc ASME Dyn Syst Control Conf. 2019. PMID: 32030310 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Preliminary Feasibility Study of a Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Function Assistance in Stroke Survivors.Front Neurosci. 2017 Oct 9;11:547. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00547. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29062267 Free PMC article.
-
Stable Grasp Control With a Robotic Exoskeleton Glove.J Mech Robot. 2020 Dec 1;12(6):061015. doi: 10.1115/1.4047724. Epub 2020 Jul 28. J Mech Robot. 2020. PMID: 34168720 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on compliant characteristics of lower extremity exoskeleton robots].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Feb 25;36(1):157-163. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201804023. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30887791 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
A Systematic Review of Low-Cost Actuator Implementations for Lower-Limb Exoskeletons: a Technical and Financial Perspective.J Intell Robot Syst. 2022;106(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s10846-022-01695-0. Epub 2022 Aug 16. J Intell Robot Syst. 2022. PMID: 35990171 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Experimental Evaluation of a Novel Portable Haptic Robotic Exoskeleton Glove System for Patients with Brachial Plexus Injuries.Rep U S. 2022 Oct;2022:11115-11120. doi: 10.1109/iros47612.2022.9981468. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Rep U S. 2022. PMID: 37303849 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Control, and Experimental Evaluation of A Novel Robotic Glove System for Patients with Brachial Plexus Injuries.IEEE Trans Robot. 2023 Apr;39(2):1637-1652. doi: 10.1109/tro.2022.3220973. Epub 2022 Nov 23. IEEE Trans Robot. 2023. PMID: 37035529 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Newly-Designed Wearable Robotic Hand Exoskeleton Based on Surface Electromyographic Signals.Front Neurorobot. 2021 Sep 15;15:711047. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2021.711047. eCollection 2021. Front Neurorobot. 2021. PMID: 34603003 Free PMC article.
-
INTEGRATED AND CONFIGURABLE VOICE ACTIVATION AND SPEAKER VERIFICATION SYSTEM FOR A ROBOTIC EXOSKELETON GLOVE.Proc ASME Des Eng Tech Conf. 2020 Aug;10:V010T10A043. doi: 10.1115/detc2020-22365. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Proc ASME Des Eng Tech Conf. 2020. PMID: 36478444 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized Voice Activated Grasping System for a Robotic Exoskeleton Glove ★.Mechatronics (Oxf). 2022 May;83:102745. doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2022.102745. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Mechatronics (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35241876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bogue, R., 2009, “Exoskeletons and Robotic Prosthetics: A Review of Recent Developments,” Industrial Robot, 36(5), pp. 421–427. 10.1108/01439910910980141 - DOI
-
- Brault, M. W., 2010, Americans with Disabilities: 2010. U.S. Census 2010 Report. https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/2012/demo/p70-131.pdf
-
- Yap, H. K., Lim, J. H., Nasrallah, F., Goh, J. C., and Yeow, R. C., 2015, “A Soft Exoskeleton for Hand Assistive and Rehabilitation Application Using Pneumatic Actuators With Variable Stiffness,” Proceedings — IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Seattle, WA, May 26–30, pp. 4967–4972.
-
- Ho, N. S., Tong, K. Y., Hu, X. L., Fung, K. L., Wei, X. J., Rong, W., and Susanto, E. A., 2011, “An EMG-Driven Exoskeleton Hand Robotic Training Device on Chronic Stroke Subjects: Task Training System for Stroke Rehabilitation,” Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, June 29–July 1. DOI: 10.1109/ICORR.2011.5975340 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
