Role of diet and lifestyle modification in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 33912410
- PMCID: PMC8059462
- DOI: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_86_20
Role of diet and lifestyle modification in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
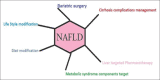
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is considered as the hepatic evidence of insulin resistance which is the hallmark of type 2 diabetes. NAFLD is considered as the risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes and has a high frequency of occurrence in those with existing type 2 diabetes. Compared with patients with only NAFLD or type 2 diabetes, these patients show a poor metabolic profile and increase mortality. Hence, effective treatment strategies are necessary. Here, we review the role of diet and lifestyle modification in the management of NAFLD and type 2 diabetes. Based on the available studies, it has been shown that the addition of any kind of physical activity or exercise is beneficial for patients with both NAFLD and type 2 diabetes. Proper dietary management leads to weight loss are also effective in improving metabolic parameters in patients with both NAFLD and type 2 diabetes. In conclusion, it is clear that increasing physical activity or exercise is effective in improving metabolic parameters in patients who are suffering with both NAFLD and type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Hepatic steatosis; Insulin resistant; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Physical activity; Type 2 diabetes.
Copyright: © 2021 Tzu Chi Medical Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: Impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–95. - PubMed
-
- Pi-Sunyer FX. The obesity epidemic: Pathophysiology and consequences of obesity. Obes Res. 2002;10(Suppl 2):97S–104S. - PubMed
-
- Haynes P, Liangpunsakul S, Chalasani N. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in individuals with severe obesity. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8:535–47, viii. - PubMed
-
- Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; National Heart, Lung, And Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources