Expanding armamentarium in advanced prostate cancer management: are all novel antiandrogens the same?
- PMID: 33912507
- PMCID: PMC8053696
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prnil.2020.03.002
Expanding armamentarium in advanced prostate cancer management: are all novel antiandrogens the same?
Abstract
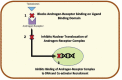
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common cancer in men. Androgen receptor axis plays a crucial role in the carcinogenesis of PCa. The mainstay treatment of prostate cancer is blockage of androgen receptor axis but in a vast majority of patient resistance to androgen deprivation therapy is inevitable. After using enzalutamide, the first new generation anti-androgen (AA), two new generation AA drugs were synthesized. New generation anti-androgen drugs are used especially in castration resistance prostate cancer. But recently, there are new publications regarding using new generation anti-androgens in castration sensitive prostate cancer patients. In this review, we will compare structure, mechanisms of effect and clinical outcomes in phase 3 trials of these new generation AA drugs.
Keywords: Androgen Receptor Antagonists; Androgen-Resistant Prostatic Cancer; Prostatic Neoplasms.
© 2020 Asian Pacific Prostate Society. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Androgen Receptor Targeted Treatments of Prostate Cancer: 35 Years of Progress with Antiandrogens.J Urol. 2018 Nov;200(5):956-966. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.04.083. Epub 2018 May 3. J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29730201 Review.
-
Androgen receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Dec;140(3):223-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23859952 Review.
-
Androgen receptor antagonists for prostate cancer therapy.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014 Aug;21(4):T105-18. doi: 10.1530/ERC-13-0545. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24639562 Review.
-
Resistance to second generation antiandrogens in prostate cancer: pathways and mechanisms.Cancer Drug Resist. 2020 Sep 17;3(4):742-761. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.45. eCollection 2020. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 35582225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Timing of androgen deprivation monotherapy and combined treatments in castration-sensitive and castration-resistant prostate cancer: a narrative review.World J Urol. 2020 Mar;38(3):601-611. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02704-y. Epub 2019 Mar 4. World J Urol. 2020. PMID: 30830274 Review.
Cited by
-
Revision of CHAARTED and LATITUDE criteria among Japanese de novo metastatic prostate cancer patients.Prostate Int. 2021 Dec;9(4):208-214. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Prostate Int. 2021. PMID: 35059359 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of dose reduction in androgen receptor pathway inhibitors for castration-resistant prostate cancer.Prostate Int. 2022 Mar;10(1):50-55. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2021.10.001. Epub 2021 Oct 30. Prostate Int. 2022. PMID: 35510101 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral Metastasis Predicts Response to New Hormonal Agents in Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer.Oncologist. 2023 Jul 5;28(7):596-603. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad102. Oncologist. 2023. PMID: 37084289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang D., Tindall D.J. Androgen action during prostate carcinogenesis. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;776:25–44. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources