Apo A1/Apo B ratio and acute coronary syndrome among peritoneal dialysis patients
- PMID: 33913384
- PMCID: PMC8901281
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1918556
Apo A1/Apo B ratio and acute coronary syndrome among peritoneal dialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is prevalent in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) patients. However, the association between the apoprotein profile and ACS is not well known. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the relationship between apoproteins and ACS in CAPD patients.
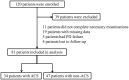
Methods: Eighty-one CAPD patients were included in this retrospective study. The primary endpoint was ACS. Predictors were baseline apoprotein levels, particularly the ratio of apoprotein A1 (Apo A1)/apoprotein B (Apo B). Cox regression was used to determine the relationship between Apo A1/Apo B and ACS.
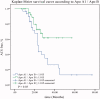
Results: During follow-up, 34 (41.98%) CAPD patients experienced an ACS. ACS patients had higher levels of total cholesterol (p = 0.03), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (p = 0.04), C-reactive protein (p = 0.01), and Apo B (p < 0.01). However, hemoglobin (p = 0.01) and Apo A1/Apo B (p < 0.01) were lower in the ACS group than the non-ACS group. Patients with Apo A1/Apo B ≥ 1.105 experienced fewer ACS compared with those with Apo A1/Apo B < 1.105 (33.33% vs. 75.56%, p = 0.03). In Cox regression, Apo A1/Apo B (RR, 0.06; 95% CI, 0.00-0.77; p = 0.03) was independently associated with ACS.
Conclusions: Apo A1/Apo B was strongly associated with ACS and may be considered as a predictor of future ACS in CAPD patients.
Keywords: Apoprotein A1; acute coronary syndrome; apoprotein B; continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was preceded by a preprinted version at
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in renal failure: the relation to mode of dialysis.Kidney Int. 1999 Apr;55(4):1536-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00375.x. Kidney Int. 1999. PMID: 10201020
-
Lipids, lipoproteins and apolipoproteins abnormalities in patients undergoing dialysis.J Tongji Med Univ. 1997;17(2):126-8. doi: 10.1007/BF02888251. J Tongji Med Univ. 1997. PMID: 9639806
-
The uremic dyslipidemia: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study.Am J Kidney Dis. 1992 Oct;20(4):324-35. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)70294-9. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992. PMID: 1415199
-
Apoprotein B/Apoprotein A-1 Ratio and Mortality among Prevalent Dialysis Patients.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 May 6;11(5):840-846. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09830915. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26912548 Free PMC article.
-
Lipids, lipoproteins and apolipoproteins A-I and B and apolipoprotein losses in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.Atherosclerosis. 1989 Sep;79(1):47-50. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90032-4. Atherosclerosis. 1989. PMID: 2803346
Cited by
-
Association of the PCSK6 rs1531817(C/A) polymorphism with the prognosis and coronary stenosis in premature myocardial infarction patients: a prospective cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jul 22;23(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02206-w. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39039525 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Daily Consumption of Functionalized Yogurts with Sacha Inchi Oil and Interspecific Hybrid Palm Oil on the Lipid Profile and ApoB/ApoA1 Ratio of Healthy Adult Subjects.Foods. 2024 Dec 9;13(23):3973. doi: 10.3390/foods13233973. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39683045 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Ratio of Apolipoprotein B to Apolipoprotein A1 With Survival in Peritoneal Dialysis.Front Nutr. 2022 Mar 25;9:801979. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.801979. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35399692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delles C, Vanholder R.. Chronic kidney disease, Clin Sci (London). 2017;131(3):225–226. - PubMed
-
- Go AS. Cardiovascular disease consequences of CKD, Semin Nephrol. 2016;36(4):293–304. - PubMed
-
- Chen T, Yang M.. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with cardiovascular disease in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;78:106063. - PubMed
-
- Anavekar NS, McMurray JJ, Velazquez EJ, et al. . Relation between renal dysfunction and cardiovascular outcomes after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(13):1285–1295. - PubMed
-
- Lingel JM, Srivastava MC, Gupta A.. Management of coronary artery disease and acute coronary syndrome in the chronic kidney disease population-a review of the current literature. Hemodial Int. 2017;21(4):472–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials