Discovery of Orally Bioavailable Purine-Based Inhibitors of the Low-Molecular-Weight Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase
- PMID: 33914534
- PMCID: PMC8939909
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02126
Discovery of Orally Bioavailable Purine-Based Inhibitors of the Low-Molecular-Weight Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase
Abstract
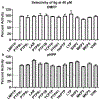
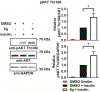
Obesity-associated insulin resistance plays a central role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. A promising approach to decrease insulin resistance in obesity is to inhibit the protein tyrosine phosphatases that negatively regulate insulin receptor signaling. The low-molecular-weight protein tyrosine phosphatase (LMPTP) acts as a critical promoter of insulin resistance in obesity by inhibiting phosphorylation of the liver insulin receptor activation motif. Here, we report development of a novel purine-based chemical series of LMPTP inhibitors. These compounds inhibit LMPTP with an uncompetitive mechanism and are highly selective for LMPTP over other protein tyrosine phosphatases. We also report the generation of a highly orally bioavailable purine-based analogue that reverses obesity-induced diabetes in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest: patent applications covering the compounds have been filed by SBP. NB and SMS have equity interests in Nerio Therapeutics, a company that may potentially benefit from the research results, and receive income from the company for consulting. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California, San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Figures

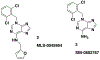




References
-
- Saltiel AR, Putting the Brakes on Insulin Signaling. N Engl J Med 2003, 349 2560–2562. - PubMed
-
- Saltiel AR; Kahn CR, Insulin Signalling and the Regulation of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Nature 2001, 414 799–806. - PubMed
-
- White MF; Shoelson SE; Keutmann H; Kahn CR, A Cascade of Tyrosine Autophosphorylation in the Beta-Subunit Activates the Phosphotransferase of the Insulin Receptor. The Journal of biological chemistry 1988, 263 2969–2980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

