HIF-2α activation potentiates oxidative cell death in colorectal cancers by increasing cellular iron
- PMID: 33914705
- PMCID: PMC8203462
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI143691
HIF-2α activation potentiates oxidative cell death in colorectal cancers by increasing cellular iron
Abstract
Hypoxia is a hallmark of solid tumors that promotes cell growth, survival, and metastasis and confers resistance to chemo and radiotherapies. Hypoxic responses are largely mediated by the transcription factors hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and HIF-2α. Our work demonstrates that HIF-2α is essential for colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. However, targeting hypoxic cells is difficult, and tumors rapidly acquire resistance to inhibitors of HIF-2α. To overcome this limitation, we performed a small molecule screen to identify HIF-2α-dependent vulnerabilities. Several known ferroptosis activators and dimethyl fumarate (DMF), a cell-permeable mitochondrial metabolite derivative, led to selective synthetic lethality in HIF-2α-expressing tumor enteroids. Our work demonstrated that HIF-2α integrated 2 independent forms of cell death via regulation of cellular iron and oxidation. First, activation of HIF-2α upregulated lipid and iron regulatory genes in CRC cells and colon tumors in mice and led to a ferroptosis-susceptible cell state. Second, via an iron-dependent, lipid peroxidation-independent pathway, HIF-2α activation potentiated ROS via irreversible cysteine oxidation and enhanced cell death. Inhibition or knockdown of HIF-2α decreased ROS and resistance to oxidative cell death in vitro and in vivo. Our results demonstrated a mechanistic vulnerability in cancer cells that were dependent on HIF-2α that can be leveraged for CRC treatment.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell stress; Hypoxia; Metabolism; Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

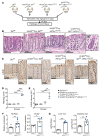
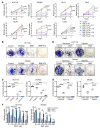


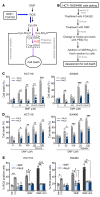
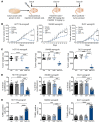
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA148828/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA248160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK097153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA237421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA215607/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA245546/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM130183/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK089503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA130810/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009676/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244931/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

