Secreted Wnt antagonists in scrub typhus
- PMID: 33914733
- PMCID: PMC8112706
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009185
Secreted Wnt antagonists in scrub typhus
Abstract
Background: The mechanisms that control local and systemic inflammation in scrub typhus have only been partially elucidated. The wingless (Wnt) signaling pathways are emerging as important regulators of inflammation and infection, but have not been investigated in scrub typhus.
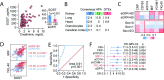
Methodology/principal findings: Plasma levels of secreted Wnt antagonists (i.e. DKK-1, sFRP-3, WIF-1 and SOST) were analyzed in patients with scrub typhus (n = 129), patients with similar febrile illness without O. tsutsugamushi infection (n = 31), febrile infectious disease controls, and in healthy controls (n = 31) from the same area of South India, and were correlated to markers of inflammation, immune and endothelial cell activation as well as for their association with organ specific dysfunction and mortality in these patients. We found i) Levels of SOST and in particular sFRP-3 and WIF-1 were markedly increased and DKK-1 decreased in scrub typhus patients at admission to the hospital compared to healthy controls. ii) In recovering scrub typhus patients, SOST, sFRP-3 and WIF-1 decreased and DKK-1 increased. iii) SOST was positively correlated with markers of monocyte/macrophage and endothelial/vascular activation as well as with renal dysfunction and poor outcome iv) Finally, regulation of Wnt pathways by O. tsutsugamushi in vitro in monocytes and ex vivo in mononuclear cells isolated from patients with scrub typhus, as evaluated by gene expression studies available in public repositories, revealed markedly attenuated canonical Wnt signaling.
Conclusions/significance: Our findings suggest that scrub typhus is characterized by attenuated Wnt signaling possibly involving dysregulated levels of several secreted pathway antagonists. The secreted Wnt antagonist SOST was strongly associated with renal dysfunction and poor prognosis in these patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Kurien Thomas was unavailable to confirm their authorship contributions. On their behalf, the corresponding author has reported their contributions to the best of their knowledge. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Canonical notch activation in patients with scrub typhus: association with organ dysfunction and poor outcome.Infection. 2024 Aug;52(4):1357-1365. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02192-2. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Infection. 2024. PMID: 38502427 Free PMC article.
-
Increased endothelial and macrophage markers are associated with disease severity and mortality in scrub typhus.J Infect. 2014 Nov;69(5):462-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.06.018. Epub 2014 Jul 1. J Infect. 2014. PMID: 24995849
-
Clinical and paraclinical profile, and predictors of outcome in 90 cases of scrub typhus, Meghalaya, India.Infect Dis Poverty. 2016 Oct 5;5(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s40249-016-0186-x. Infect Dis Poverty. 2016. PMID: 27716337 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging trends of scrub typhus disease in southern Rajasthan, India: A neglected public health problem.J Vector Borne Dis. 2022 Oct-Dec;59(4):303-311. doi: 10.4103/0972-9062.342357. J Vector Borne Dis. 2022. PMID: 36751761 Review.
-
Investigations of seasonal outbreaks of acute encephalitis syndrome due to Orientia tsutsugamushi in Gorakhpur region, India: A One Health case study.Indian J Med Res. 2021 Mar;153(3):375-381. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_625_21. Indian J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33907001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of four immune-related signatures in keloid.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 27;13:942446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.942446. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35967426 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces sclerostin secretion by extracellular vesicle via TLR4/miR-92a-3p/PTEN/NF-κB signalling pathway in murine macrophage.Inflamm Res. 2025 Jan 25;74(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01987-1. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39862242
References
-
- Tantibhedhyangkul W, Prachason T, Waywa D, El Filali A, Ghigo E, Thongnoppakhun W, et al.. Orientia tsutsugamushi stimulates an original gene expression program in monocytes: relationship with gene expression in patients with scrub typhus. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011;5:e1028. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

